Post by : Layla Badr
New research has uncovered yet another way that spaceflight affects the human body. Scientists have discovered that traveling to space can speed up the aging of blood-forming stem cells, which are essential for maintaining healthy blood and a strong immune system. These findings come from a NASA-funded study that analyzed stem cells sent to the International Space Station (ISS) on four SpaceX resupply missions.
Study Design and Method
The research involved stem cell samples flown on four different SpaceX resupply missions to the ISS, specifically in December 2021, July 2022, November 2022, and March 2023. To understand the effects of spaceflight, the scientists carefully monitored stem cells from the bone marrow of individual donors in real-time during these missions. The changes observed in space were compared with samples that remained on Earth from the same donors.
Stay informed with the latest news. Follow DXB News Network on WhatsApp Channel
By studying these samples, researchers were able to track exactly how space conditions affected the stem cells over periods of 30 to 45 days. This allowed them to see direct changes caused by microgravity, radiation, and other spaceflight factors, rather than relying on indirect observations.
Key Findings: How Spaceflight Affects Stem Cells
The results of the study showed several important changes in the stem cells after their time in space:
Reduced Ability to Form New Cells:
The cells that traveled to space lost some of their capacity to produce healthy new blood cells. This reduction in regenerative ability means the body may struggle to replace old or damaged blood cells efficiently.
Increased DNA Damage:
Spaceflight exposed the stem cells to higher levels of DNA damage. DNA is the genetic material in cells, and damage to it can lead to diseases like cancer or interfere with the cells’ ability to function correctly.
Accelerated Aging:
The ends of the chromosomes in the stem cells, called telomeres, showed signs of faster aging. Telomeres protect genetic information during cell division, and their shortening is a hallmark of cellular aging.
The scientists concluded that these changes were primarily caused by the combination of microgravity—the weightlessness experienced in space—and the increased radiation exposure astronauts face outside the Earth’s protective atmosphere.
What Are Stem Cells and Why Are They Important?
Stem cells are unique cells in the body that can develop into different types of cells. The specific stem cells studied here are called hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, which are found in the bone marrow inside our bones. These cells are responsible for producing all types of blood cells:
Red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body
White blood cells that fight infections and protect the body from diseases
Platelets that help the blood clot when injuries occur
If these cells stop functioning properly, it can have serious effects on overall health. For example, the body may struggle to repair tissue damage, fight infections, or detect and eliminate cancer cells. Over time, this can even affect a person’s lifespan.
How Space Affects Stem Cells
During space missions, the stem cells showed signs of becoming overactive. Normally, stem cells have periods of rest that allow them to regenerate and maintain their ability to create new cells over time. In space, however, they depleted their reserves too quickly, reducing their long-term regenerative potential.
The cells also showed increased stress and inflammation in their mitochondria. Mitochondria are the structures in cells that produce energy, and when they are stressed, the cell cannot function as efficiently. Additionally, parts of the genome usually kept silent, known as the “dark genome,” became active, which can lead to instability and further cell stress.
Interestingly, the study found differences in how stem cells from different donors responded to spaceflight. According to Dr. Catriona Jamieson, senior author of the study and a professor of medicine at the University of California San Diego, some individuals’ stem cells showed natural resilience and were able to withstand space stress better than others. This variability suggests that certain anti-aging factors might be present in some people’s cells but not in others.
Radiation and Microgravity: The Main Culprits
On Earth, we are protected from cosmic radiation by the planet’s atmosphere and magnetic field. In space, this protection is gone. Astronauts are exposed to high-energy radiation that can damage DNA and increase risks for:
Cancer
Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s
Cardiovascular problems
Immune system disorders
In addition to radiation, the microgravity environment in space leads to other health issues such as:
Loss of bone density
Muscle atrophy
Changes in blood flow and organ function
These combined factors create a unique challenge for the human body, especially during long-duration missions such as trips to Mars or extended stays on the ISS.
Implications for Astronaut Health
Understanding how spaceflight affects blood-forming stem cells is crucial for keeping astronauts healthy during long missions. These findings may help scientists develop strategies to protect astronauts from the harmful effects of space travel. This could include targeted treatments to strengthen stem cells, protect DNA, or reduce stress in mitochondria during missions.
Dr. Jamieson emphasized that studying these stem cell changes not only helps space medicine but also provides insights into human aging and diseases on Earth, including cancer. By observing how space accelerates certain cellular processes, researchers can better understand how aging and cellular stress affect everyone.
Future Research
The researchers are continuing to study stem cell responses during ongoing SpaceX resupply missions to the ISS. They aim to identify key resilience factors that could be enhanced before, during, and after space travel to improve human health in space and on Earth.
This ongoing research may one day allow astronauts to maintain healthier blood and immune systems during long journeys, while also offering new insights into how to slow aging and improve stem cell function on Earth.
This study clearly shows that spaceflight has profound effects on the human body at the cellular level. Blood-forming stem cells, which are essential for health and immunity, age faster and become more stressed in space. While these findings are particularly important for astronauts, they may also help scientists develop new treatments for age-related diseases and improve human health on Earth. The work underscores the challenges of human space travel and the importance of continued research into protecting the body in extreme environments.

IGCF 2025 in Sharjah: Global Leaders Unite for Better Life
IGCF 2025 begins at Expo Centre Sharjah, uniting 237 speakers to discuss food, health, education, su

Sandro Tonali Scores Injury-Time Winner as Italy Beat Israel
Italy snatched a thrilling 5-4 win over Israel in World Cup qualifiers with Sandro Tonali scoring a

Sandro Tonali Scores Injury-Time Winner as Italy Beat Israel
Italy snatched a thrilling 5-4 win over Israel in World Cup qualifiers with Sandro Tonali scoring a
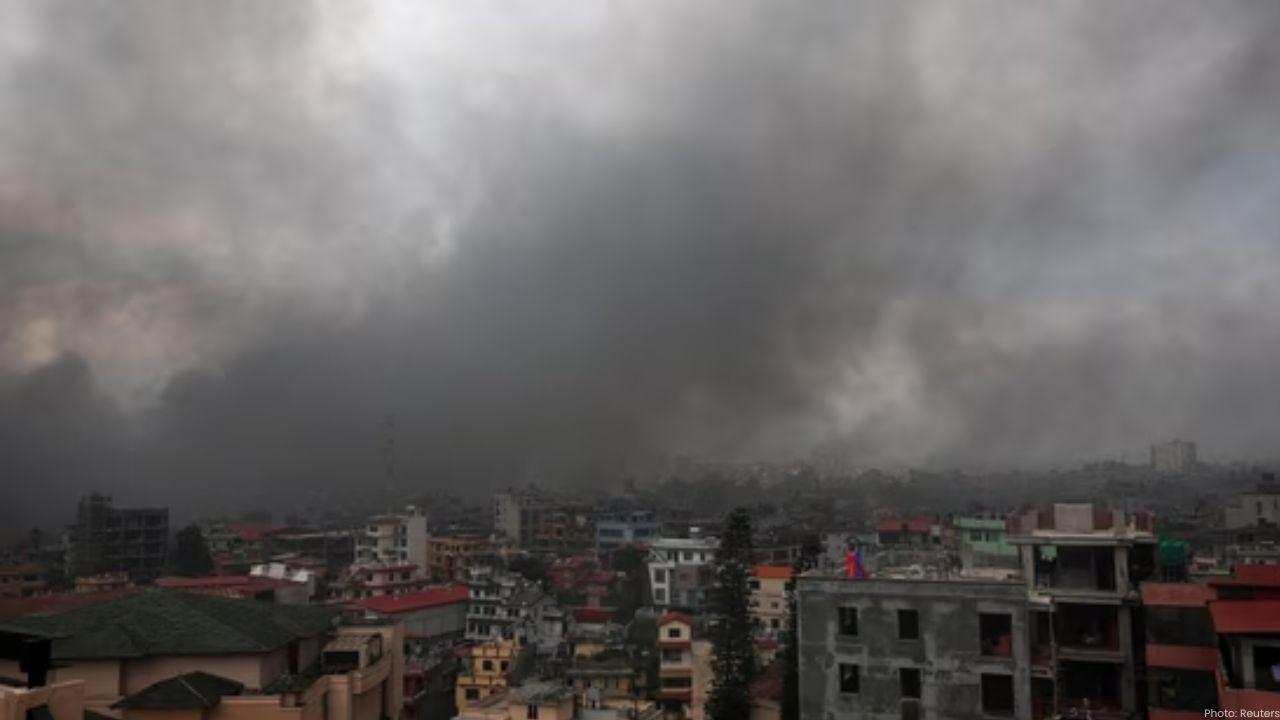

Nepal Protests: Kathmandu Airport Closed Amid Gen Z Agitation
Nepal's Kathmandu faces violent Gen Z protests over social media ban; 19 dead, airport closed, fligh

Monsoon Alert 7 Vegetables to Avoid for a Healthy Rainy Season
Avoid these 7 vegetables during monsoon to stay healthy prevent stomach issues and enjoy a safe n
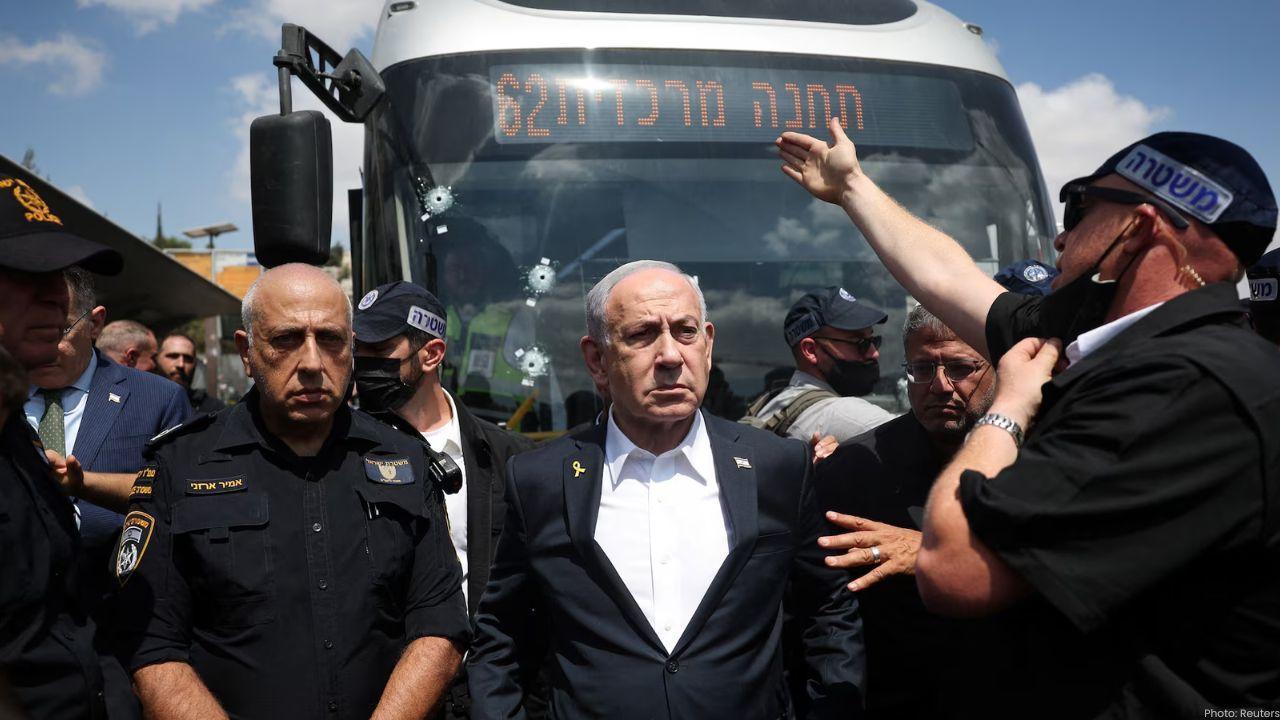

Deadly Jerusalem Attack Kills Six, Eight Injured by Gunmen
Six Israelis were killed and eight wounded in a shooting attack at Jerusalem’s Ramot Junction. Israe
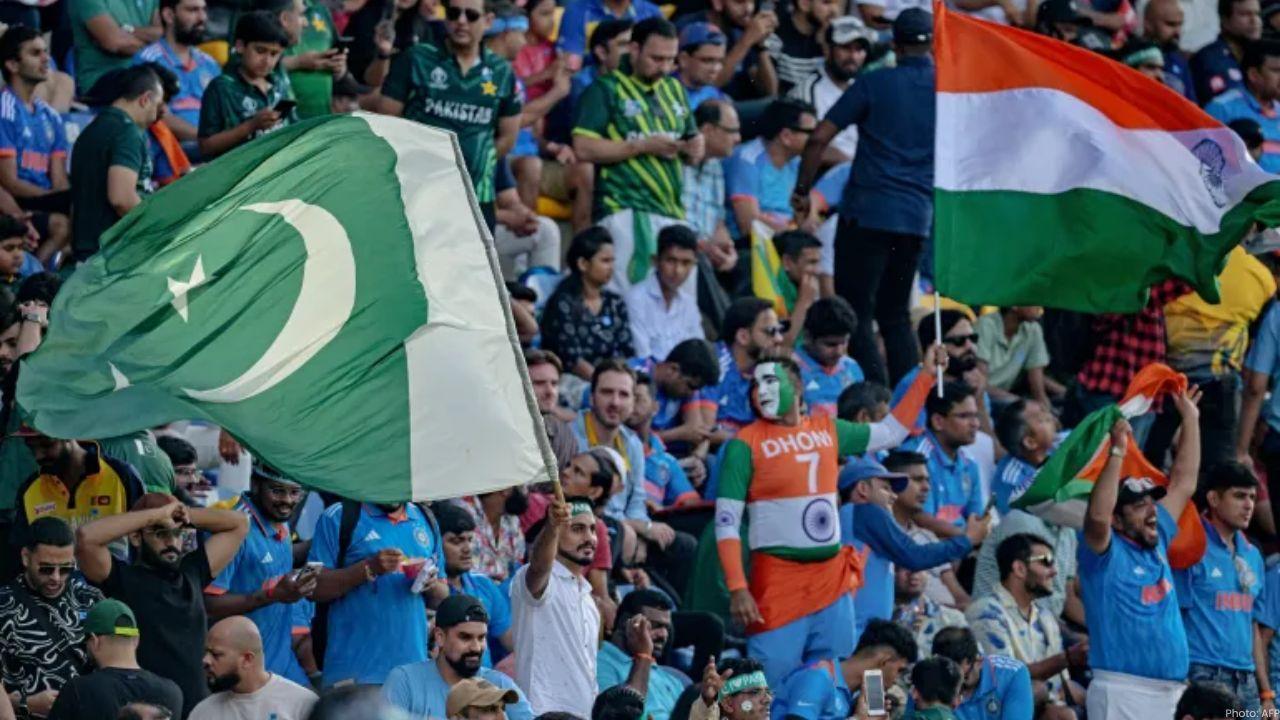

Asia Cup 2025: India vs Pakistan Clash in Dubai Sparks Excitement
Asia Cup 2025 kicks off in Dubai. Fans eagerly await India vs Pakistan clash amid political tension.

At Least 60 Dead in Night Attack on Village in Nigeria’s Borno State
Armed fighters attack Darul Jamal village in Nigeria, killing over 60, including soldiers as residen

Ronaldo Shines with Two Goals as Portugal Beats Armenia 5-0
Cristiano Ronaldo scored twice as Portugal started World Cup qualifying with a 5-0 win over Armenia

Justin Bieber Drops Eighth Studio Album Swag II Fans Excited
Justin Bieber surprises fans with Swag II, his eighth album featuring 23 new tracks and collaboratio

Venice Film Festival 2025 ends with surprise winners and strong messages
Jim Jarmusch’s film wins Golden Lion at Venice Film Festival 2025, amid strong performances emotiona

Kurt Russell Joins Yellowstone Spinoff 'The Madison' as Star & Producer
Kurt Russell returns to TV in Yellowstone spinoff 'The Madison', joining Michelle Pfeiffer in a stor

Australia funds $72M for medical research in Asia-Pacific
Australia invests $72M to support medical research, vaccines, and health solutions across Southeast

UPU launches solution to restart US mail delivery
Mail to the US dropped 80% after duty-free exemption ended; UPU launches a tool to calculate duties

UAE karate team shines with silver and bronze at Asian event
UAE athletes Sheikha Al Yafei and Rashid Al Suraidi win silver and bronze at the Asian Karate Champi