
Post by : Anis Karim
For centuries, the Moon has fascinated humanity. From myths and legends to telescopes and rockets, it has always been the closest celestial body symbolizing our cosmic aspirations. The Apollo missions of the 1960s and 70s gave humans the first taste of lunar exploration, but no permanent presence was established. Now, half a century later, the dream of building lasting lunar settlements is being revived on a global scale.
Today, governments and private companies are investing billions in developing technologies to support human life on the Moon. Plans include lunar bases for scientific research, mining for rare minerals, and even acting as a launch pad for Mars missions. The target year often cited is 2030—a symbolic marker by which nations hope to achieve permanent lunar footholds. But how realistic is this timeline, and what progress has been made so far?
The United States is spearheading efforts with NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return astronauts to the Moon by 2026. Unlike the Apollo missions, Artemis is designed for sustainability. Its goals include establishing a lunar base camp where astronauts can live and work for extended periods.
The program will deploy the Lunar Gateway, a space station orbiting the Moon, serving as a hub for missions, supplies, and scientific experiments. From this gateway, astronauts can descend to the lunar surface using advanced landers. The Artemis Base Camp is envisioned to include habitation modules, rovers, and power systems to support long-term stays.
By the 2030s, NASA hopes to use this base as a stepping stone to Mars. Permanent human presence on the Moon is not just a symbolic achievement but a practical necessity for testing life-support systems, radiation shielding, and closed-loop habitats needed for interplanetary travel.
China has emerged as a formidable player in space exploration. Through its Chang’e lunar program, China has achieved remarkable milestones, including landing rovers on the Moon’s far side. Its long-term plan involves building an International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), in collaboration with Russia.
This proposed station would include robotic and crewed modules, power systems, and scientific labs. Construction could begin in the late 2020s, with operational bases expected in the 2030s. Unlike NASA’s Artemis, which is U.S.-led and open to allies, the ILRS is intended as an alternative space partnership, especially for countries outside the Artemis Accords.
China’s ambitious goals are backed by strong political will and consistent funding. If realized, their lunar base could rival NASA’s efforts and ignite a new era of space competition reminiscent of the Cold War space race.
The European Space Agency (ESA) is also deeply invested in lunar exploration. It has proposed the concept of a “Moon Village,” where nations collaborate to build habitats, share resources, and conduct research. ESA envisions this as a cooperative effort, with multiple partners contributing technologies ranging from 3D-printed lunar habitats to solar power systems.
Japan, through its space agency JAXA, has also announced plans for lunar bases, focusing on sustainable water extraction and energy solutions. India, following its Chandrayaan missions, is also expected to join global efforts, though on a smaller scale. These collaborations highlight that permanent lunar presence is not just a national ambition but a shared human goal.
Beyond governments, private companies are reshaping lunar exploration. SpaceX, led by Elon Musk, plays a key role in NASA’s Artemis missions with its Starship lunar lander. Musk envisions long-term colonization of Mars, but establishing a Moon base is a critical step toward that vision.
Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos, has proposed the Blue Moon lander and dreams of millions of people living and working in space. Bezos sees the Moon as a key site for mining resources, particularly water ice, which can be converted into fuel for deep space missions.
Other companies like Astrobotic and Intuitive Machines are developing robotic landers to deliver cargo and experiments to the lunar surface. Their contributions may seem small compared to national programs, but they form the foundation of a future lunar economy.
Despite the enthusiasm, establishing permanent lunar settlements is fraught with challenges.
Radiation Exposure: The Moon lacks a protective atmosphere and magnetic field, exposing astronauts to harmful cosmic rays and solar radiation. Developing adequate shielding—through underground habitats or regolith-based shelters—is critical.
Temperature Extremes: Lunar days and nights each last about 14 Earth days, with temperatures soaring to 127°C in sunlight and dropping to –173°C in darkness. Habitats and power systems must withstand these extremes.
Lack of Atmosphere: With no breathable air, every resource—oxygen, water, and food—must either be transported from Earth or produced locally.
Psychological Stress: Isolation, confined spaces, and distance from Earth pose mental health challenges for astronauts living on the Moon.
Costs and Logistics: Building, transporting, and maintaining lunar bases require astronomical budgets and innovative supply chains. Without international cooperation and private investment, sustaining long-term presence may prove difficult.
One of the most promising discoveries for lunar settlement is the existence of water ice at the Moon’s poles. These reserves could be harvested for drinking water, oxygen, and hydrogen fuel. If successfully extracted, lunar water could dramatically reduce reliance on Earth-based supply missions.
This potential resource has fueled renewed interest in the Moon, with multiple missions planned to map and test water extraction technologies. Whoever develops reliable methods first may gain a decisive advantage in the race to establish permanent lunar bases.
Transporting building materials from Earth is impractical due to cost and weight. Instead, space agencies are exploring the use of lunar regolith—the dusty soil covering the Moon—for 3D printing habitats.
This approach could create durable shelters with radiation protection. Robots could be deployed first to construct habitats before humans arrive, reducing risk. ESA has already tested 3D-printed prototypes using simulated lunar soil on Earth. If scaled successfully, it could revolutionize space architecture.
The Moon is not just a scientific outpost but also a potential economic frontier. Rare minerals, such as helium-3—a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion—could make the Moon a valuable resource hub. Furthermore, lunar settlements could act as refueling stations for spacecraft heading deeper into the solar system.
The development of a lunar economy could resemble Earth’s early colonies, with trade, mining, and technological innovation driving expansion. Private companies are especially eager to tap into this new frontier, as it could open trillion-dollar industries in space.
While the vision of permanent lunar bases by 2030 is ambitious, experts remain cautiously optimistic. NASA plans to land astronauts by 2026 and establish Artemis Base Camp soon after. China’s ILRS could begin construction in the late 2020s, with partial operations by the early 2030s.
Realistically, by 2030, we may see semi-permanent habitats—capable of hosting astronauts for months at a time—rather than fully developed lunar cities. These bases will serve as proof of concept, paving the way for larger, more permanent settlements in the following decades.
The pursuit of lunar bases is not just about exploration; it’s about survival and progress. Earth faces challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and overpopulation. The Moon offers a testing ground for technologies that could one day allow humanity to expand beyond its home planet.
Moreover, the Moon inspires a sense of unity. Just as Apollo 11 united the world in awe, the establishment of lunar bases could become a symbol of global cooperation. While competition exists between nations, the larger goal is to extend human presence into the cosmos.
This article is for informational and editorial purposes only. While based on ongoing space programs and expert projections, the timelines and plans discussed remain subject to technological, financial, and political developments.

Open Masters Games Abu Dhabi 2026 Opens with Grand Ceremony
Sheikh Zayed bin Mohamed attended the opening of Open Masters Games Abu Dhabi 2026, welcoming 25,000

Arab Hope Makers 2025 Finale in Dubai on Feb 15
Arab Hope Makers will hold its 6th edition closing ceremony on Feb 15 in Dubai. The winner will rece

Ben Sulayem Hosts Paraguay President for Luxury Car Drive
FIA President Mohammed Ben Sulayem welcomed Paraguay President Santiago Peña in Dubai, offering a sp

US, Philippines Sign Deal to Build Critical Minerals Supply Chain
The US and Philippines signed a new MOU to develop critical minerals and rare earths, aiming to boos
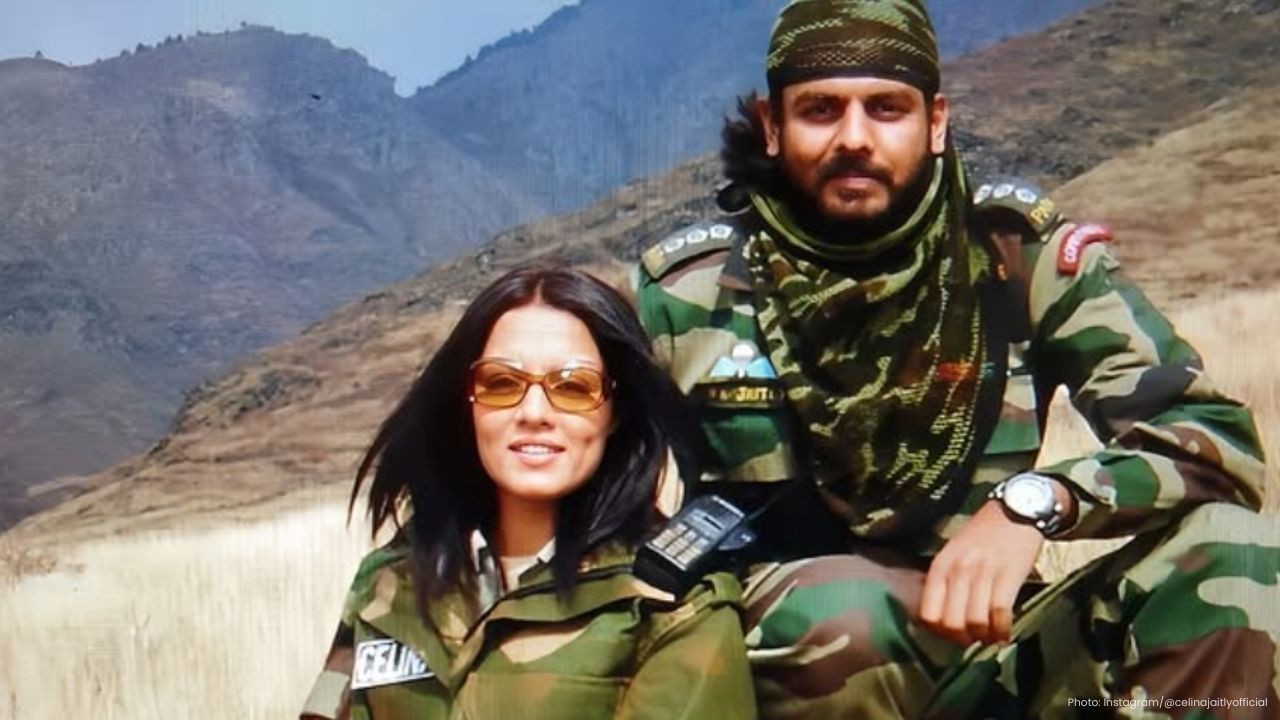

Celina Jaitly Says Brother Detained in UAE for 17 Months
Actor Celina Jaitly claims her ex-army officer brother Vikrant Jaitly has been detained in UAE since

Abu Dhabi to Launch Electric Seagliders for Coastal Travel by 2028
Abu Dhabi partners with VERSA to introduce zero-emission Seagliders by 2028, cutting coastal travel
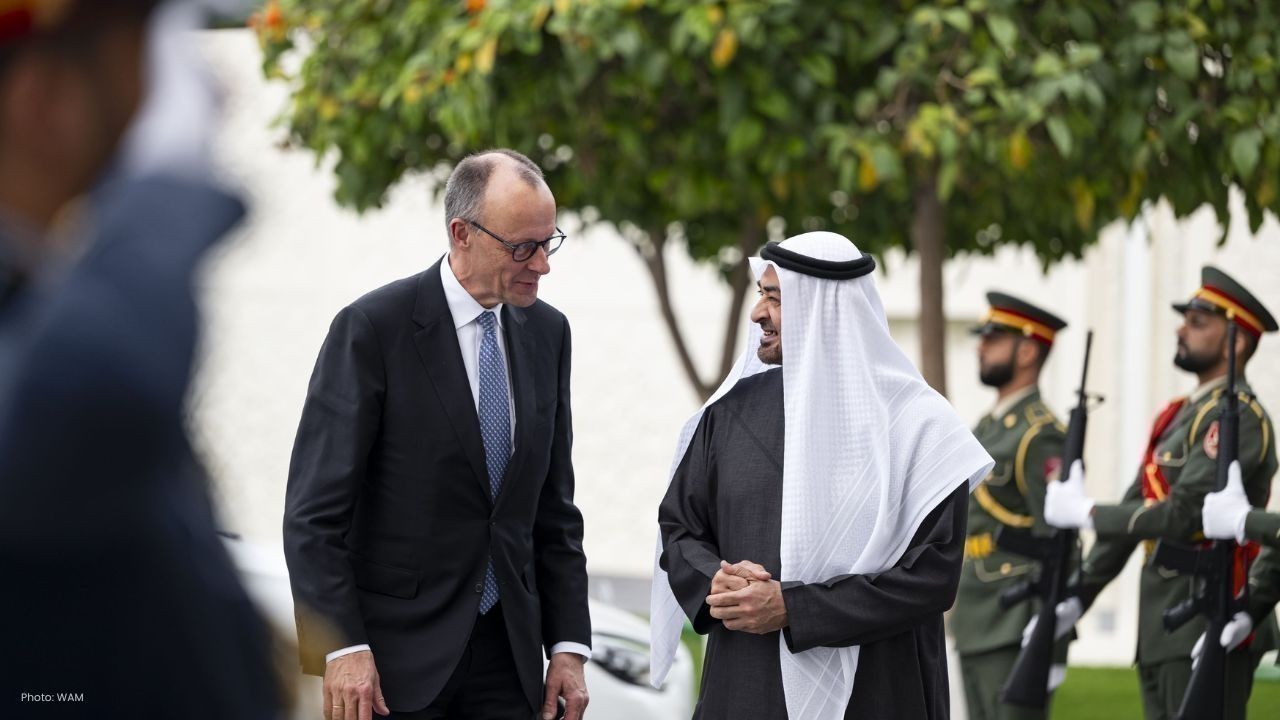

UAE President Meets Germany’s Merz, Signs Key MoUs
UAE President Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed met German Chancellor Friedrich Merz in Abu Dhabi to boost co

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
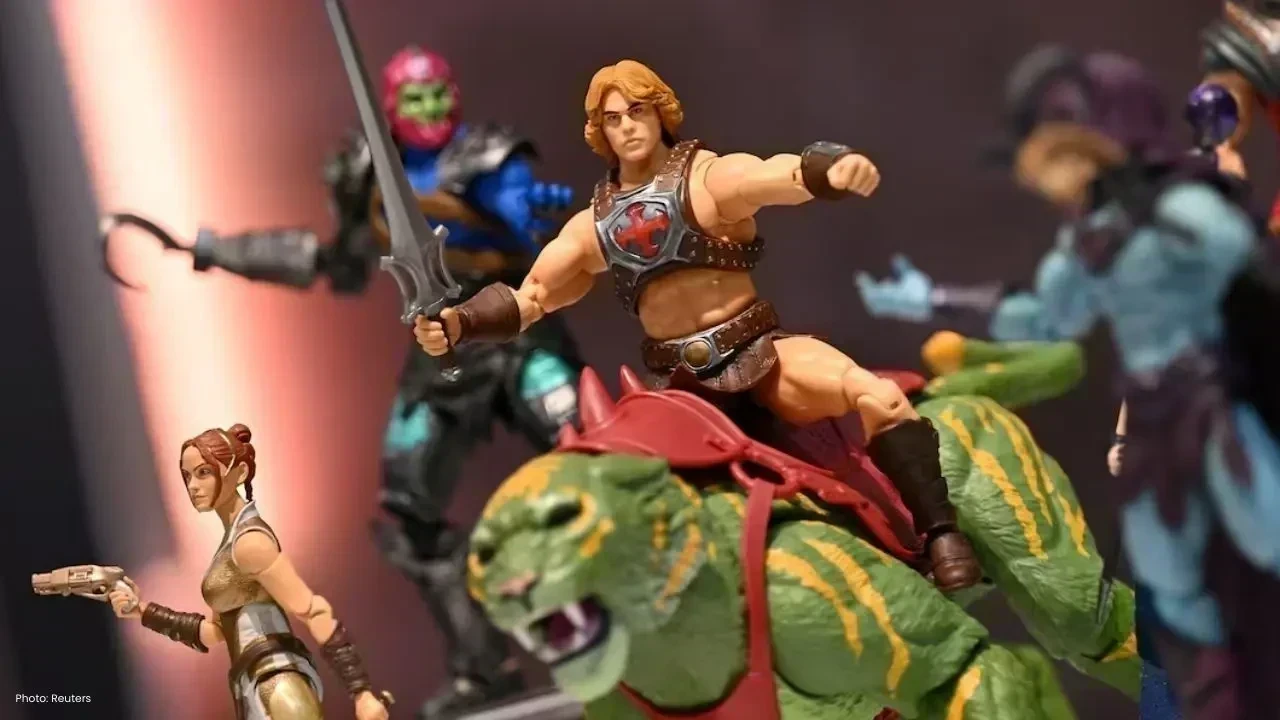

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin