
Post by : Naveen Mittal
Discipline in schools is no longer seen as mere punishment for misbehavior. Modern frameworks emphasize student well-being, restorative practices, and behavior support systems. The focus is on understanding root causes, providing guidance, and fostering accountability, rather than enforcing authority alone.
Across various systems, policymakers are moving away from punitive tactics—like corporal punishment, humiliation, or exclusion—toward constructive approaches that promote self-regulation, social skills, and positive relationships. The goal is to build safe, respectful, and emotionally healthy learning environments.
In Abu Dhabi, for example, authorities have recently banned ten traditional forms of punishment and introduced a tiered disciplinary framework. Schools now classify student misconduct into multiple levels and prescribe permitted corrective actions, while rejecting practices that harm dignity or well-being.
Under the updated policy, allowed actions include verbal or written warnings, parent meetings, supervised removal from class, temporary suspension (in serious cases), or community service. Techniques such as physical punishment, public shaming, withholding food or water, or deducting grades are expressly prohibited.
To support this change, schools are being instructed to prioritize intervention, reflection, counseling, and parental engagement before resorting to discipline.
Further, the UAE has strengthened legal penalties for bullying or neglect in schools: institutions and individuals may now face fines, license suspensions, or even criminal consequences if violations occur. This demonstrates a heightened emphasis on student protection.
Elsewhere, India and other countries are also rethinking disciplinary rules. Some states are encouraging progressive discipline, mental health support, and stricter supervision of student conduct. In many developing regions, the challenge is replacing entrenched punitive methods with supportive systems.
Schools must transparently define acceptable behavior standards, responsibilities, and norms. A code of conduct should be shared with students, parents, and staff, laying out categories of misconduct and proportional responses.
Discipline becomes much easier when behavior is shaped proactively. This includes:
Teaching social-emotional skills (empathy, conflict resolution, self-control)
Having class charters or student-driven behavioral agreements
Recognizing and reinforcing positive behavior (through praise, privileges, leadership roles)
Peer mentoring, student councils, and leadership programs
Not all infractions are equal. A multi-level model helps:
Level One: Minor issues (e.g. tardiness, uniform violation) → verbal warning, reflection
Level Two: Repeated misbehavior or moderate misconduct → counseling, parent meeting
Level Three: Bullying, cheating, property damage → suspension, more serious interventions
Level Four: Very severe acts (violence, weapons, cybercrime) → formal inquiry, exclusion or legal action
This helps ensure consistency, fairness, and that responses match the severity.
Instead of shame and exclusion, many schools are adopting restorative approaches: dialogues, mediation, student responsibility, peer conferencing, or collaborative resolution. Reflection circles or restorative justice sessions help students repair harm and reintegrate.
Behavior often signals deeper emotional or social issues. Behavior policy must be linked to counseling, social work, psychological support, mentorship programs, and referral systems to help students manage stress, trauma, or conflict.
Discipline is not the school’s burden alone. Policies must include parent involvement, transparent communication, training for teachers, and mechanisms for feedback and appeal. Community norms and cultural sensitivity also matter.
A policy is only as effective as its implementation. Schools must invest in:
Training staff to apply rules consistently, fairly, and empathetically
Monitoring disciplinary decisions and ensuring accountability
Periodic review of policy effectiveness, feedback loops, and deterrent removal of bias
Improves school climate, safety, and emotional well-being
Reduces student alienation, dropouts, and behavior recidivism
Builds student self-regulation, interpersonal skills, and responsibility
Enhances trust among students, teachers, and families
Aligns discipline with modern educational goals (holistic development, well-being)
Requires sustained investment in training, counseling, and oversight
If inconsistently enforced, it may erode trust or invite accusations of favoritism
Shifting from punitive to supportive systems can be slow and face resistance
High variability in staff buy-in or readiness
In contexts with large student populations and limited resources, implementation may be uneven
Context Audit & Stakeholder Input
Assess prevailing discipline practices, cultural norms, student behavior trends, resource gaps, and engage teachers, students, and parents.
Policy Drafting & Customization
Create codes of conduct, categorize misconduct levels, define permissible responses, and integrate restorative components and support mechanisms.
Professional Development & Orientation
Train teachers, staff, and administrators on behavior de-escalation, conflict resolution, trauma-informed approaches, restorative practices, and consistent application.
Pilot & Feedback Loop
Test the policy in select classrooms or schools, monitor outcomes, collect feedback on clarity, fairness, and impact, and adjust before full rollout.
Full Rollout with Support Structures
Launch across the institution with clarity, resources, counseling availability, communication materials, and oversight frameworks.
Monitoring & Refinement
Use quantitative and qualitative data—incident logs, student surveys, behavior trends, stakeholder feedback—to refine rules, training needs, and policy gaps.
Start by modeling calm, respectful responses to misbehavior
Use data and behavioral insights (which times, contexts, student groups) to preempt issues
Regularly review behavior logs to identify patterns and tailor interventions
Celebrate positive behavior publicly to build culture
Involve students in crafting class norms and implications
Provide spaces for student voice, conflict mediation, feedback
Use flexible responses: time-out, quiet space, mediation—not only punishments
Ensure backup from leadership so teachers feel supported in enforcing policies
Document every disciplinary action with rationale and follow-up
Adjust policies over time with evolving needs, culture, and student maturity
In a strong move toward student protection, Abu Dhabi’s education authority has banned ten disciplinary practices deemed harmful or degrading and established a clear behavior classification system with permitted measures. The emphasis is shifting from punishment to guidance, reflection, and accountability.
Moreover, UAE authorities have made bullying and neglect punishable by steep fines, institution suspensions, or criminal penalties. Schools now must proactively design safe environments and respond promptly to complaints.
These changes reflect a broader trend in the region: moving away from harmful disciplinary traditions (like corporal punishment or public humiliation) toward student-centered, restorative, and legally protected frameworks.
Importantly, in the UAE, all forms of corporal punishment are strictly prohibited under existing educational and child protection laws, reinforcing a culture where dignity and well-being must prevail in school discipline.
This article is for general informational purposes and does not serve as legal or policy guidance. Educational institutions’ discipline laws, child protection rules, and behavioral frameworks differ by country, region, and school board. Always consult relevant laws, educational authorities, and qualified professionals when designing or revising discipline policies.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
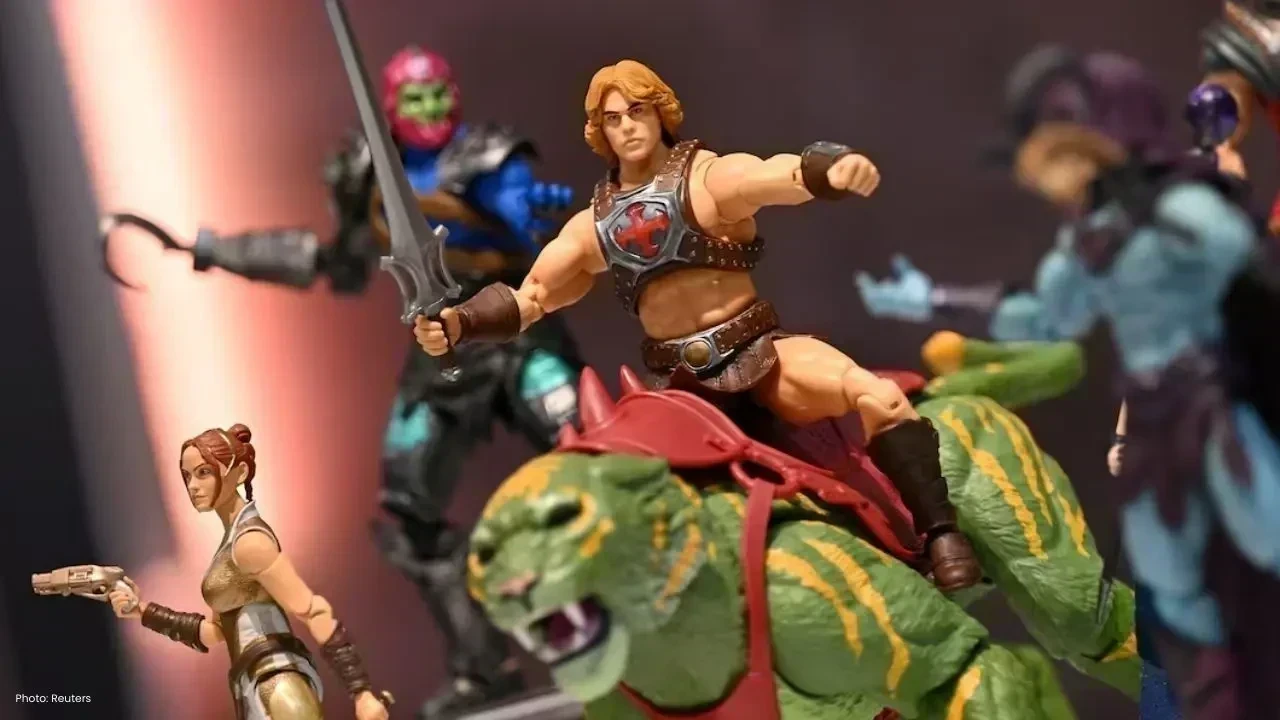

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin