Post by : Anis Karim
The global population is projected to surpass 9.8 billion by 2050, creating unprecedented demand for protein. Traditional livestock farming, while effective for centuries, is increasingly unsustainable due to its environmental footprint, resource consumption, and ethical concerns.
To meet these challenges, innovators are exploring alternative protein sources, ranging from lab-grown meat to edible insects and novel plant-based proteins. These options promise to address environmental sustainability, food security, and health, marking a profound shift in how humans source and consume protein.
Alternative proteins are no longer niche products for early adopters — they are entering mainstream markets as consumers, corporations, and governments recognize the urgent need for sustainable food systems.
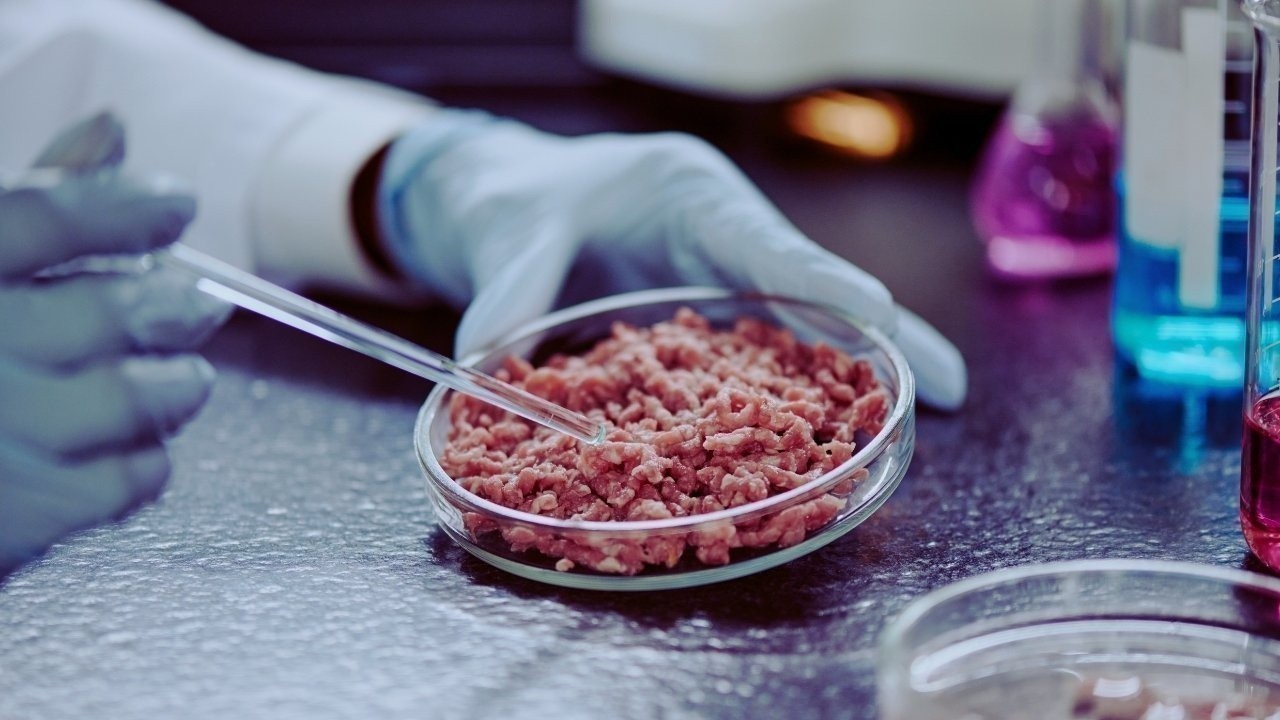
Lab-grown, or cultured, meat is produced by cultivating animal cells in controlled environments, bypassing the need for traditional livestock. The process involves extracting muscle cells from an animal and allowing them to grow in nutrient-rich bioreactors, eventually forming edible meat products.
Lab-grown meat offers several advantages. It drastically reduces greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to conventional meat production. Additionally, it eliminates the ethical concerns associated with animal slaughter and can be engineered to meet nutritional requirements, such as optimized protein content and reduced saturated fat.
Countries such as Singapore have approved lab-grown meat for commercial sale, while startups in the United States, Israel, and the Netherlands are scaling production for global markets. Despite initial high costs, economies of scale and technological advances are expected to make cultured meat increasingly affordable.
Insects have long been consumed in many cultures, from Africa and Asia to parts of Latin America. They are rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals, yet require far less land, water, and feed than conventional livestock.
Species such as crickets, mealworms, and black soldier fly larvae are being processed into protein powders, snacks, and even meat analogs. Companies worldwide are creating cricket-based protein bars, insect flour for baking, and mealworm burgers, making entomophagy — the practice of eating insects — more palatable to Western consumers.
In addition to environmental benefits, insects produce minimal greenhouse gases and efficiently convert feed into protein. Their integration into food systems could significantly reduce the ecological footprint of global protein consumption.
Plant-based protein has surged in popularity, driven by consumer demand for ethical and sustainable alternatives. Soy, pea, and wheat proteins form the foundation of plant-based burgers, sausages, and dairy substitutes.
Advances in food technology now allow plant proteins to mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of animal products more convincingly than ever before. Companies are experimenting with blends of legumes, grains, and algae to produce protein-rich products suitable for diverse diets.
Beyond taste, plant-based proteins are accessible, scalable, and compatible with existing agricultural systems. They also contribute to reducing reliance on intensive livestock farming, further supporting sustainability goals.
Algae and microbial proteins represent a promising frontier in alternative nutrition. Microalgae, such as spirulina and chlorella, are highly efficient at photosynthesis, producing protein-rich biomass with minimal land and water requirements.
Similarly, single-cell proteins derived from yeast, bacteria, or fungi can be cultivated in controlled environments to produce high-quality protein. These methods allow rapid scaling, reduce reliance on arable land, and can be fortified with vitamins and minerals, offering a nutritionally complete solution.
Countries in Asia and Europe are investing in algae farms and microbial protein startups, recognizing their potential for sustainable, high-protein food production in both human diets and animal feed.
One of the main drivers for alternative protein adoption is environmental sustainability. Traditional livestock farming contributes significantly to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for roughly 14–18% of global emissions.
Lab-grown meat can reduce land use by up to 99% and water usage by 82–96%, while insects require less than 10% of the feed needed for conventional livestock. Plant-based proteins and microbial proteins also demand fewer resources and emit fewer pollutants, making them key solutions to mitigate climate change.
As the world seeks to reduce its ecological footprint, alternative proteins could play a pivotal role in creating resilient, environmentally conscious food systems.
Alternative proteins not only offer environmental benefits but also present opportunities for improving human health. Lab-grown meat can be engineered to contain less saturated fat or enriched with essential nutrients, while plant-based proteins often provide fiber and antioxidants absent in traditional meat.
Edible insects are nutrient-dense, rich in protein, iron, zinc, and healthy fats. Microbial proteins and algae provide complete amino acid profiles, offering options for vegetarians, vegans, and those with dietary restrictions.
However, widespread adoption also requires careful monitoring for allergens, microbiological safety, and nutritional adequacy, particularly in processed or blended foods.
Alternative proteins are experiencing rapid growth in global markets. Investment in startups producing lab-grown meat, plant-based alternatives, and insect protein has surged, signaling investor confidence. Market research projects that the alternative protein sector could reach hundreds of billions of dollars in value by 2035.
Consumer acceptance is a critical factor. While early adopters in North America and Europe embrace plant-based and cultured products, broader adoption depends on taste, price parity, and cultural familiarity. Marketing, education, and product innovation will shape how mainstream these foods become.
In emerging markets, insects and plant-based proteins may integrate more naturally into traditional diets, while lab-grown meat could initially cater to premium or health-conscious segments.
Despite promise, alternative proteins face challenges. Lab-grown meat production remains costly, energy-intensive, and technologically complex. Regulatory approval, labeling standards, and public perception vary across countries, affecting market rollout.
Insects face cultural barriers, particularly in Western countries where entomophagy is less common. Consumer education, innovative product formats, and culinary creativity are essential to overcome hesitation.
Plant-based proteins, while popular, may face limitations in texture and flavor replication, particularly for sensitive products like sausages or cheeses. Scaling production without compromising quality, nutrition, or sustainability is an ongoing concern.
Infrastructure, supply chain logistics, and regulatory clarity are critical to ensuring these foods are safe, accessible, and economically viable on a global scale.
Governments and international organizations are increasingly supporting alternative protein research and commercialization. Singapore has positioned itself as a hub for lab-grown meat, offering regulatory pathways and funding for startups. The European Union funds research projects on plant-based and microbial proteins, emphasizing sustainability and innovation.
Countries in Asia, Africa, and South America are integrating edible insects and plant-based proteins into nutrition programs to combat food insecurity. Policy incentives, subsidies, and public-private partnerships are accelerating adoption, highlighting the role of governance in shaping the future of food.
The future of food is unlikely to be dominated by a single alternative; instead, a combination of lab-grown meat, plant-based proteins, insects, and microbial sources will coexist to meet global demands. Hybrid products blending multiple protein sources may emerge, balancing taste, nutrition, and environmental impact.
Technology will continue to drive innovation. AI-driven food design, fermentation techniques, and bioreactors will optimize production efficiency, flavor profiles, and nutrient content. Consumer feedback and sustainability metrics will guide the evolution of products that are both acceptable and beneficial for society.
As awareness grows, dietary patterns may shift, reducing dependence on traditional livestock while embracing diverse, sustainable protein options.
Alternative proteins represent a transformative opportunity to address the pressing challenges of the 21st century: environmental sustainability, food security, and public health. Lab-grown meat, edible insects, plant-based proteins, and microbial innovations each offer unique advantages, and their combined adoption could reshape global food systems.
While challenges remain in scaling production, cost reduction, consumer acceptance, and regulatory alignment, momentum is undeniable. As technology advances, investments increase, and cultural acceptance grows, the future of food looks more diverse, sustainable, and ethical.
The journey toward embracing alternative proteins is not just about innovation — it is about securing a resilient, nutritious, and environmentally conscious food supply for generations to come.
This article is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute professional, nutritional, or investment advice. The insights reflect current global trends in alternative proteins and may evolve with technological, regulatory, and market developments.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
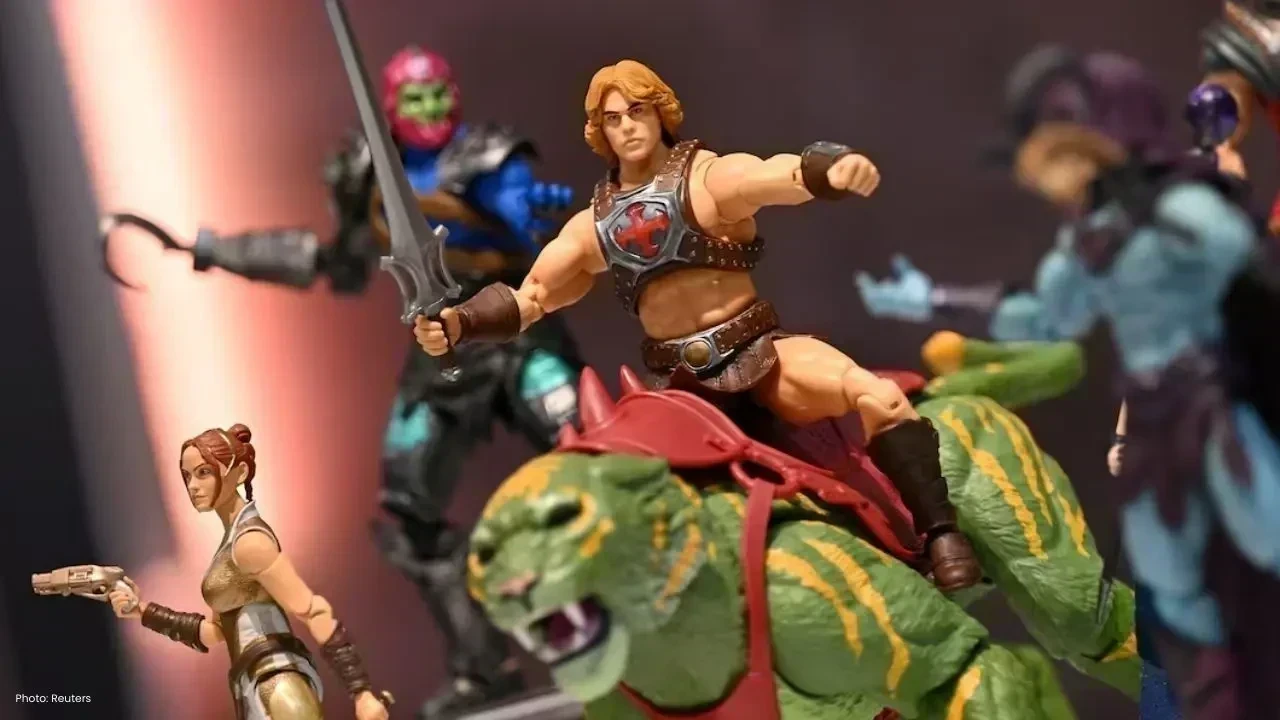

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin