
Post by : Anis Karim
A concerning contradiction is emerging worldwide. Despite having the largest youth demographic in history, countless young individuals are jobless, underemployed, or engaged in precarious jobs. Concurrently, numerous economies are experiencing slowdowns, some populations are aging, and technology is reshaping job creation and elimination.
Youth joblessness has transitioned from a temporary economic challenge linked to cycles or recessions to a chronic issue, intricately tied to demographic pressures, educational gaps, automation, and policy stagnation. For policymakers, this presents not just an economic dilemma but a significant social and political threat.
Youth unemployment typically defines those aged between 15 and 29 actively seeking jobs but unable to secure them. However, this term often obscures deeper issues such as informal jobs, unpaid roles, and positions lacking stability or growth.
In numerous regions, official unemployment statistics fail to capture this crisis's true extent. A significant number of youth have withdrawn from the job market, having given up their search due to repeated failures.
While developing nations grapple with the challenge of generating enough jobs for their growing youth demographic, advanced economies face a distinct issue. The rise of automation, outsourcing, and evolving skill demands have diminished traditional job openings for younger workers.
This compounded crisis has molded youth unemployment into a phenomenon that the world must reckon with.
Nations with substantial youth demographics often undergo what is termed a demographic bulge. Theoretically, this can lead to economic growth through an active young workforce. However, in reality, without sufficient job opportunities, it morphs into a potential source of instability.
An economy that cannot accommodate its young population will see rising unemployment, overstressed public services, and growing social discontent.
Conversely, certain areas are rapidly aging, with a shrinking pool of working-age individuals. Ironically, youth in these demographics continue to face job scarcity due to rigid job markets, high skill barriers, and limited entry-level opportunities.
This discrepancy heightens the overall tension between population needs and labor market access.
Economic growth is becoming increasingly less labor-intensive. Technological advancements enable companies to expand production without proportionately increasing their labor force.
Thus, even as economies grow, job creation frequently fails to keep up with population growth, especially among younger entrants.
Across many nations, educational institutions still emphasize degrees over practical skills. Graduates often step into the workforce with qualifications misaligned with market demands, causing employers to hesitate in hiring and resulting in consistent rejections for youth.
This misalignment of skills remains a critical contributor to youth unemployment.
Automation and AI have disproportionately affected positions historically filled by young individuals. Jobs in clerical work, retail, and basic manufacturing are increasingly automated.
This scenario diminishes the avenues through which young people can acquire initial work experience.
While new positions are being created, they frequently necessitate specialized competencies, digital literacy, and adaptability. Many young individuals lack access to training suited for these roles.
Consequently, a widening gap emerges between available opportunities and the preparedness of the youth.
Chronic unemployment significantly impacts mental health. Young individuals facing repeated rejection commonly experience anxiety, depression, and diminished self-worth.
This often results in social disengagement, eroding community connections and heightening feelings of isolation.
Joblessness delays pivotal life decisions such as marriage, home ownership, and starting a family, consequently affecting demographic trends like declining birth rates and aging populations.
The individual toll of unemployment ultimately escalates into a societal issue over time.
High youth unemployment levels have historically correlated with civil unrest. When young people feel excluded from economic prospects, their frustration often translates into protests, strikes, and political radicalization.
Numerous global movements have roots in economic exclusion and job insecurity.
Chronic joblessness undermines confidence in governments, educational systems, and economic frameworks. Young people are increasingly questioning the effectiveness of existing systems.
The erosion of this trust carries significant long-term ramifications for democratic stability and governance.
Confronted with limited opportunities at home, many young people opt for migration. This can alleviate immediate pressures but often results in a brain drain for the countries of origin.
In receiving nations, integrating young migrants into the labor force poses further challenges.
As skilled youth migrate, countries vie for talent through immigration policies, exacerbating inequality across regions.
Migration thus acts as both a symptom and a catalyst for demographic stress.
In numerous cultures, young women face specific cultural, social, and institutional barriers to employment. Even when educated, they often find themselves excluded from the workforce due to caregiving expectations or safety concerns.
This exclusion constitutes a significant economic loss.
When young women are marginalized, economies fail to fully harness their demographic potential. Tackling gender disparities is thus vital in addressing youth unemployment.
Governments typically respond with short-lived job initiatives or public employment programs. While these can be beneficial, they do not address root problems like skills mismatches or the need for private sector job creation.
In the absence of strategic long-term planning, such initiatives provide only fleeting solutions.
Educational reforms often progress slowly, remain bureaucratic, and sometimes diverge from real market demands. As industries evolve more rapidly than academic curricula, young people find themselves unprepared.
This gap continues the cycle of unemployment.
Education systems should transition toward skill-based learning, vocational training, and continuous skill development. Collaborations between educational bodies and employers can bridge existing gaps.
Early exposure to practical skills can enhance job prospects.
Promoting youth entrepreneurship can lead to job creation rather than merely job-seeking. Access to funding, mentorship, and regulatory support is essential for success.
Entrepreneurship fosters resilience and cultivates an innovative spirit.
Employers need to reconsider stringent experience requirements that alienate young applicants. Structured apprenticeship and training programs can offer essential pathways to job market entry.
Inclusive hiring practices benefit both companies and society as a whole.
Organizations that prioritize training young employees establish sustainable talent pipelines. This mitigates skill shortages and enhances workforce stability.
Youth unemployment translates into diminished productivity and slowed economic growth. Entire economies suffer when a generation remains underutilized.
The long-term ramifications far outweigh the immediate costs of implementing solutions.
Persistent youth unemployment exacerbates inequalities across generations. Young individuals entering adulthood face fewer resources, less job security, and diminished earnings potential over a lifetime.
This inequality can significantly impact economic trajectories for years to come.
Certain countries have effectively lowered youth unemployment through targeted skills initiatives, labor market adaptability, and private sector involvement.
These cases demonstrate that demographic stress is manageable when sound policies are in place.
Successful strategies often share common traits: adaptability, early intervention, and coordinated efforts between government, education, and industry.
Demographic trends will increasingly dictate economic success. Nations that fail to integrate young people into their labor forces may experience stagnation and upheaval.
Conversely, those that succeed gain a competitive advantage.
Confronting youth unemployment transcends social welfare; it has become an economic imperative. How societies choose to include youth will shape their resilience in a fast-evolving world.
Youth joblessness and demographic pressures stand out as pressing challenges for today’s global economy. A zealous generation eager to contribute is being hindered by systemic barriers, outdated norms, and sluggish policy progress.
The cost of neglecting this crisis extends beyond growth losses; it includes dwindling societal connections, escalating instability, and crumbling trust. Addressing this issue requires unified efforts, forward-thinking approaches, and a reimagination of how economies prepare youth for forthcoming challenges.
Thus, it is no longer a matter of whether youth unemployment is an issue, but whether the world can afford to postpone effective solutions.
Disclaimer:
This content is purely informative and not intended as economic, employment, or policy counsel. Readers should connect with industry experts and authentic data sources for decision-making purposes.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
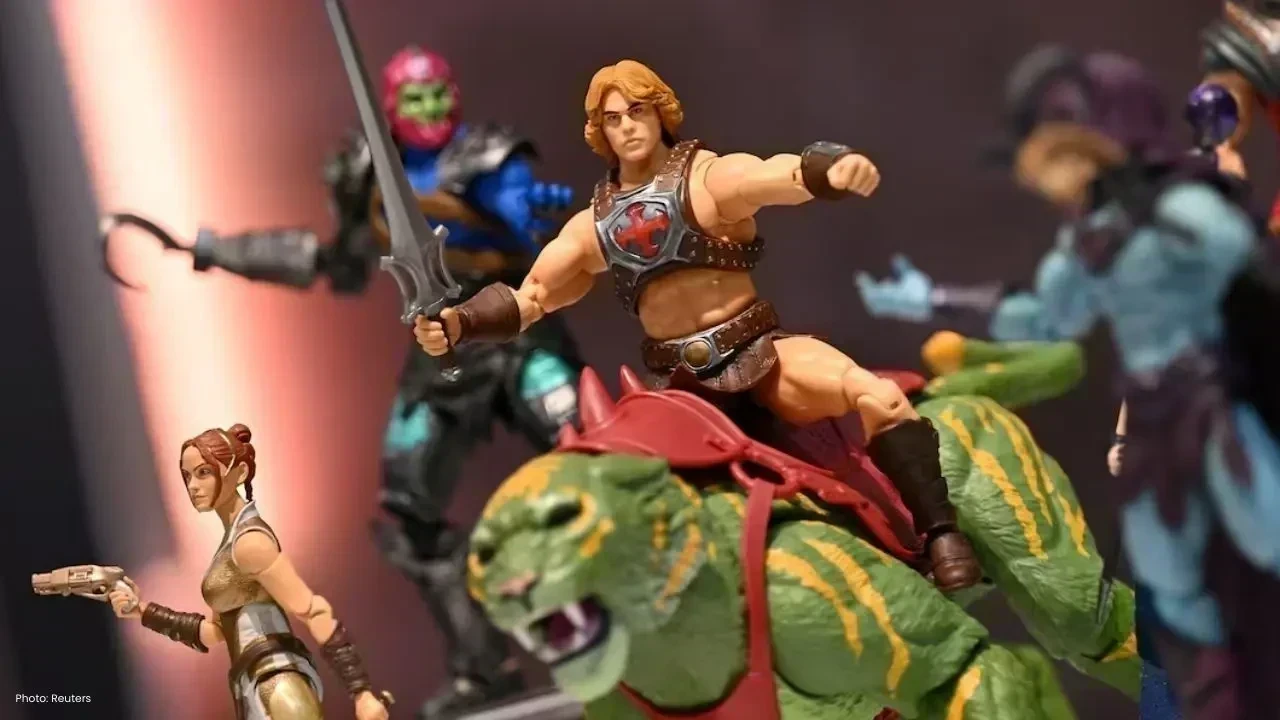

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin