
Post by : Anis Karim
In 2025, education is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the integration of spatial computing technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). These innovations are moving beyond traditional screen-based interactions, offering immersive learning experiences that bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds. Spatial computing enables students to engage with content in dynamic, interactive environments, fostering deeper understanding and retention.
Spatial computing refers to the use of technology to create digital environments that interact with the physical world. In educational settings, this involves the application of AR and VR to develop immersive learning experiences. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the learner's perception of their environment, while VR creates entirely digital environments that simulate real or imagined worlds. Together, these technologies enable students to interact with 3D models, conduct virtual experiments, and explore complex concepts in an engaging manner.
The effectiveness of spatial computing in education is supported by advancements in hardware and software. Devices such as VR headsets and AR glasses provide the necessary interfaces for immersive experiences. Software platforms offer tools for creating and managing interactive content, allowing educators to design customized learning modules that align with curriculum objectives. Additionally, developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing the adaptability and responsiveness of these technologies, enabling personalized learning experiences.
Traditional teaching methods often struggle to capture and maintain student interest. Spatial computing addresses this challenge by providing interactive and immersive learning experiences. For instance, students can explore ancient civilizations through VR simulations or manipulate molecular structures in 3D using AR applications. Such hands-on experiences make learning more engaging and enjoyable, leading to increased motivation and participation.
Abstract concepts in subjects like science and mathematics can be challenging for students to grasp. Spatial computing allows these concepts to be visualized and interacted with in three dimensions, facilitating a deeper understanding. For example, students can observe the process of photosynthesis in a virtual plant or explore the human circulatory system in 3D, making complex ideas more accessible and comprehensible.
Spatial computing enables the simulation of real-world scenarios that would be difficult or impossible to recreate in a traditional classroom. Students can conduct virtual chemistry experiments, practice surgical procedures in a controlled VR environment, or explore the surface of Mars through AR applications. These simulations provide practical experience and prepare students for real-life challenges in a safe and controlled setting.
Spatial computing has the potential to democratize education by overcoming geographical limitations. Students in remote or underserved areas can access high-quality educational content through VR and AR technologies, participating in virtual field trips, attending remote lectures, and collaborating with peers worldwide. This accessibility fosters a more inclusive learning environment, ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to succeed.
The adaptability of spatial computing technologies makes them valuable tools for supporting students with diverse learning needs. Customizable settings, such as adjustable text sizes, audio narration, and sensory-friendly modes, allow these technologies to cater to individual requirements. For students with disabilities or those requiring additional support, AR and VR can provide tailored learning experiences that enhance engagement and comprehension.
The successful integration of spatial computing into education requires educators to possess the necessary skills and knowledge. Professional development programs focused on AR and VR technologies are essential for equipping teachers with the tools to effectively incorporate these technologies into their teaching practices. Training should encompass both technical proficiency and pedagogical strategies to maximize the impact of spatial computing on student learning.
To fully realize the benefits of spatial computing, it must be seamlessly integrated into the curriculum. Educators should collaborate with curriculum developers to design learning modules that incorporate AR and VR technologies, aligning with educational standards and objectives. This integration ensures that spatial computing enhances, rather than disrupts, the learning process, providing students with meaningful and relevant experiences.
Implementing spatial computing in educational settings necessitates significant investment in technology and infrastructure. Schools must ensure they have the necessary hardware, such as VR headsets and AR devices, as well as robust internet connectivity to support these technologies. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and technical support are crucial to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of spatial computing tools.
The financial implications of adopting spatial computing can be substantial. Schools must allocate resources for the procurement of devices, software licenses, and professional development programs. While the long-term benefits of enhanced learning outcomes may justify the initial investment, careful budgeting and resource planning are essential to ensure sustainable implementation.
The use of spatial computing technologies involves the collection and processing of data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Educational institutions must establish clear policies and protocols to protect student information and comply with relevant data protection regulations. Transparency and accountability are key to maintaining trust and safeguarding the interests of students and educators.
The field of spatial computing is rapidly evolving, with continuous advancements in AR and VR technologies. Future developments may include more immersive and realistic simulations, enhanced interactivity, and greater accessibility through the use of wearable devices and cloud-based platforms. These innovations have the potential to further transform education, providing students with richer and more engaging learning experiences.
As spatial computing technologies mature, their applications in education are likely to expand. Beyond K-12 and higher education settings, AR and VR can be utilized in vocational training, adult education, and lifelong learning initiatives. These technologies offer opportunities for skill development and professional growth, catering to diverse learning needs across various stages of life.
Spatial computing, encompassing AR and VR technologies, is reshaping the educational landscape in 2025. By providing immersive, interactive learning experiences, these technologies enhance engagement, accessibility, and understanding. While challenges such as technical requirements, cost, and data security must be addressed, the potential benefits of spatial computing in education are profound. As technology continues to advance, spatial computing will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of learning, preparing students for a dynamic and interconnected world.
The information provided in this article reflects the state of spatial computing technologies in education as of 2025. Technological advancements are ongoing, and future developments may further influence the applications and impact of AR and VR in educational settings.
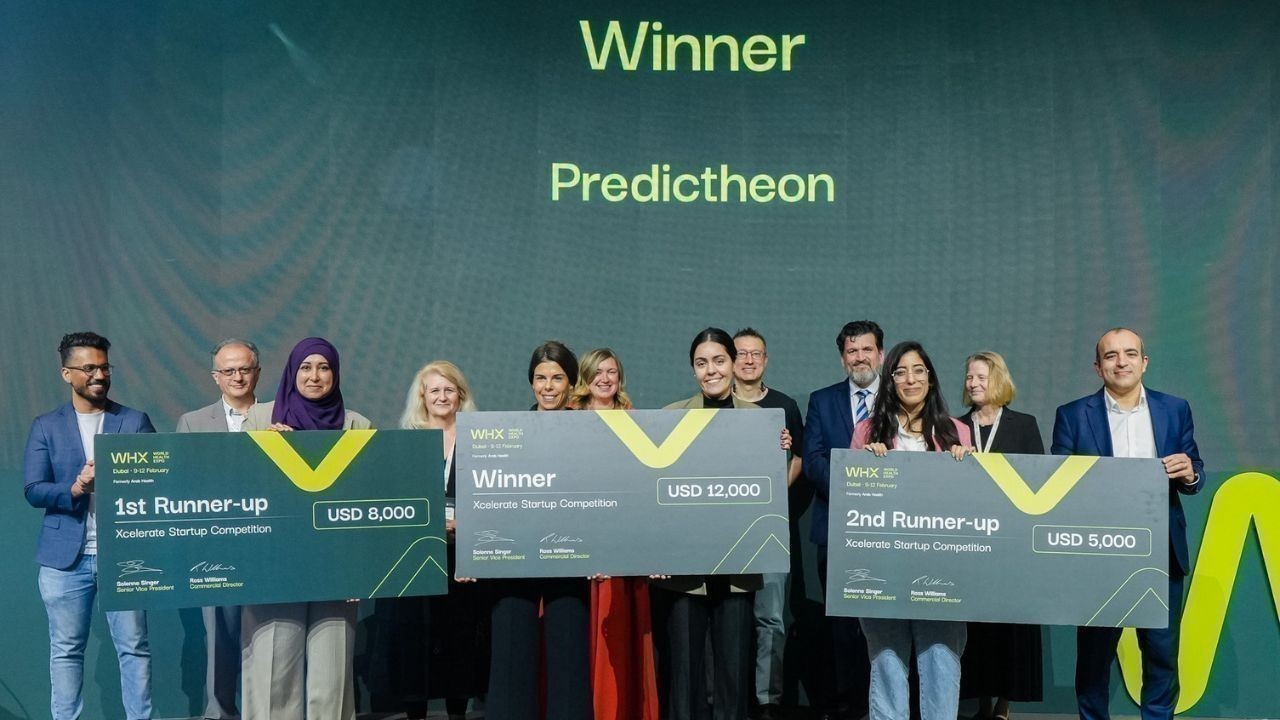

Predictheon Wins WHX Xcelerate Innovation Champion 2026
Predictheon won WHX 2026 Xcelerate, earning US$12,000, WHX 2027 space and global exposure for its AI

Omantel Launches Otech to Drive Oman’s Future Tech Vision
Omantel launches Otech to accelerate Oman’s digital transformation, strengthen data sovereignty, exp

Daimler Truck MEA Honors Top Distributors at EliteClass 2025
Daimler Truck MEA hosted EliteClass Awards 2025 in Dubai, honoring top distributors across 19 catego
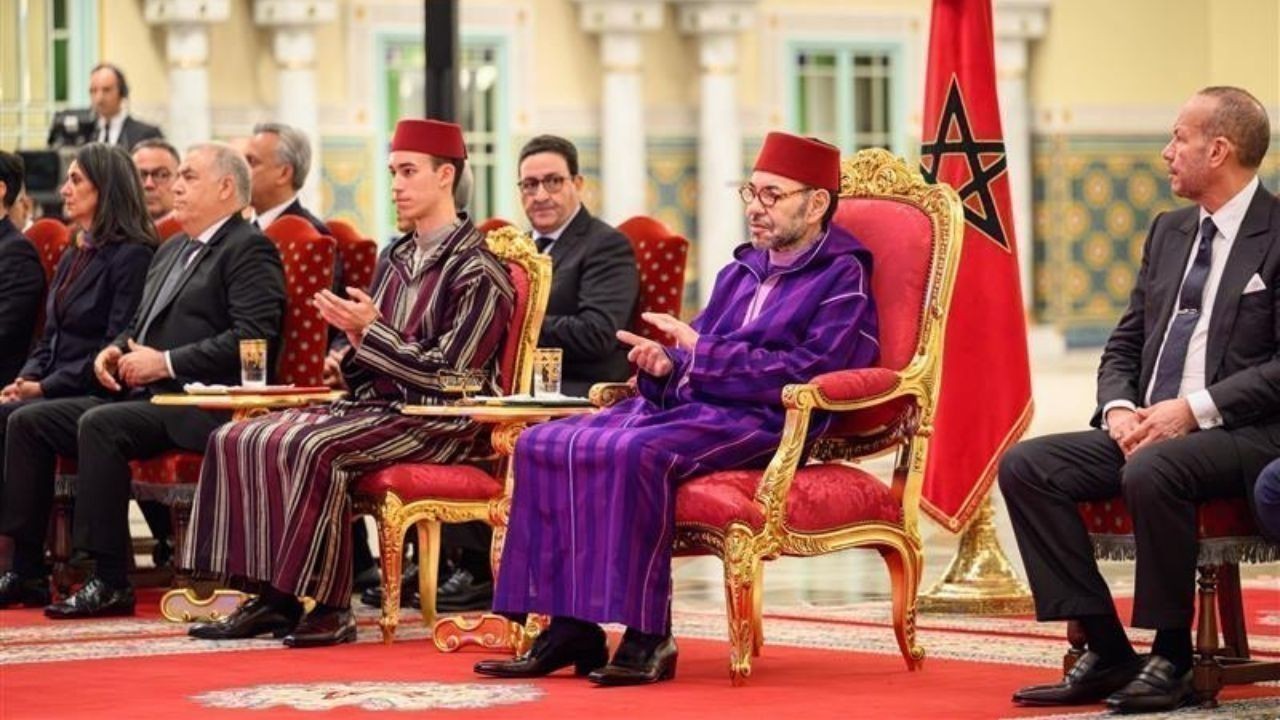

King Mohammed VI Launches Safran Landing Gear Plant in Morocco
Morocco strengthens its aerospace leadership as King Mohammed VI launches Safran’s €280M landing gea
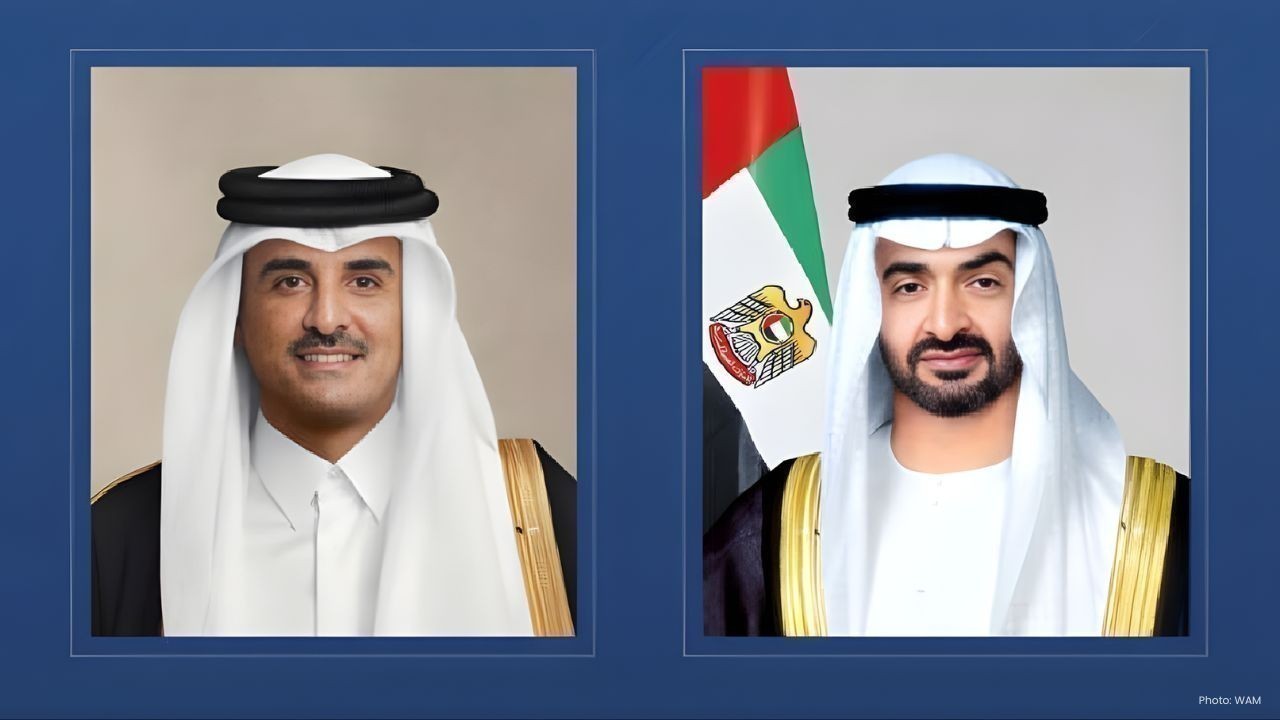

Qatar Emir Sheikh Tamim Arrives in UAE on Fraternal Visit
Qatar’s Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani arrived in Abu Dhabi on Saturday. UAE President Sheikh
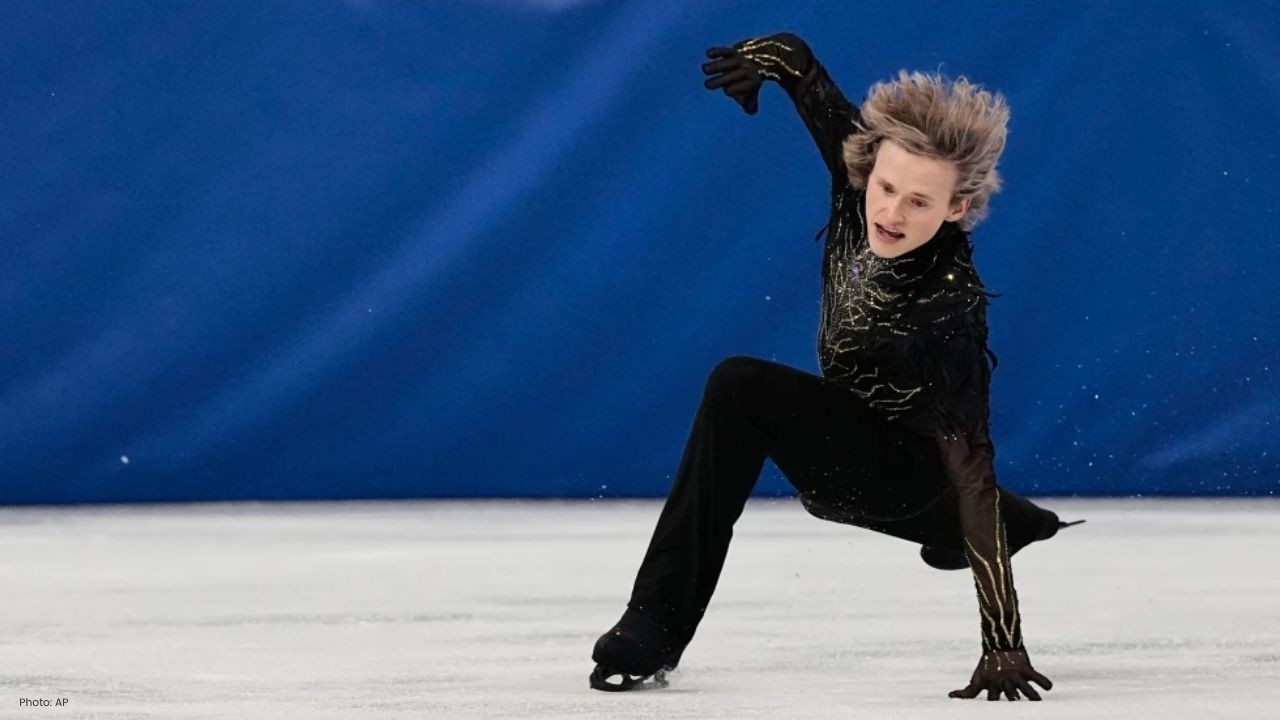

Shaidorov Wins Stunning Olympic Gold as Malinin Falters
Kazakhstan’s Mikhail Shaidorov won men’s figure skating gold after US star Ilia Malinin fell twice.
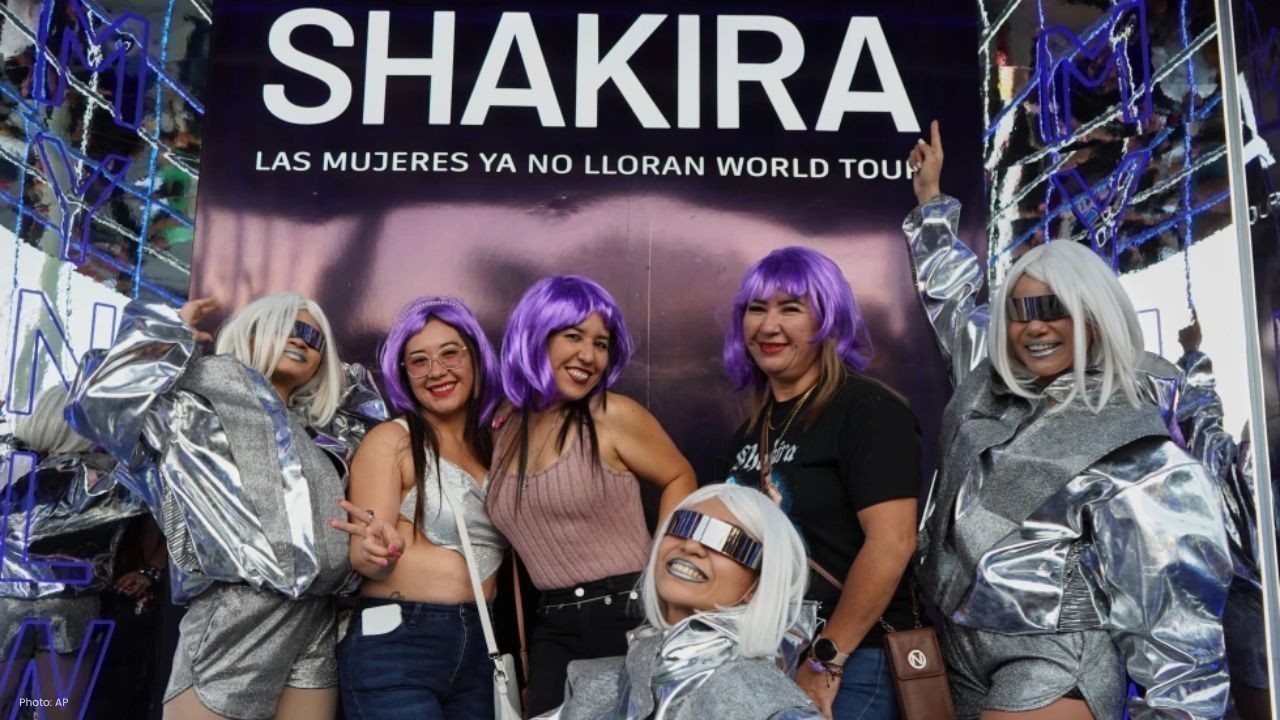

Shakira’s 5-Show El Salvador Residency Boosts Bukele Image
Shakira’s five sold-out concerts in San Salvador highlight El Salvador’s security shift under Bukele

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
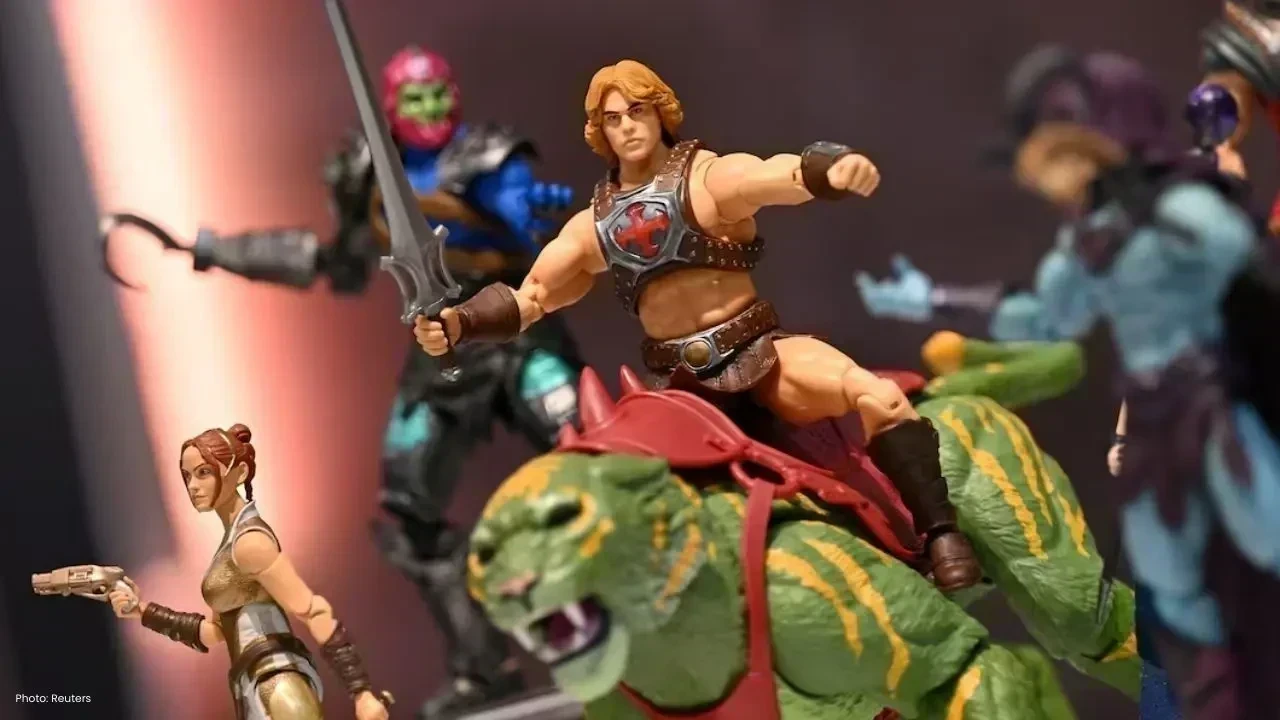

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin

China Executes 11 Members of Infamous Ming Family Behind Myanmar Scam Operations
China has executed 11 Ming family members, linked to extensive scams and gambling in Myanmar, causin