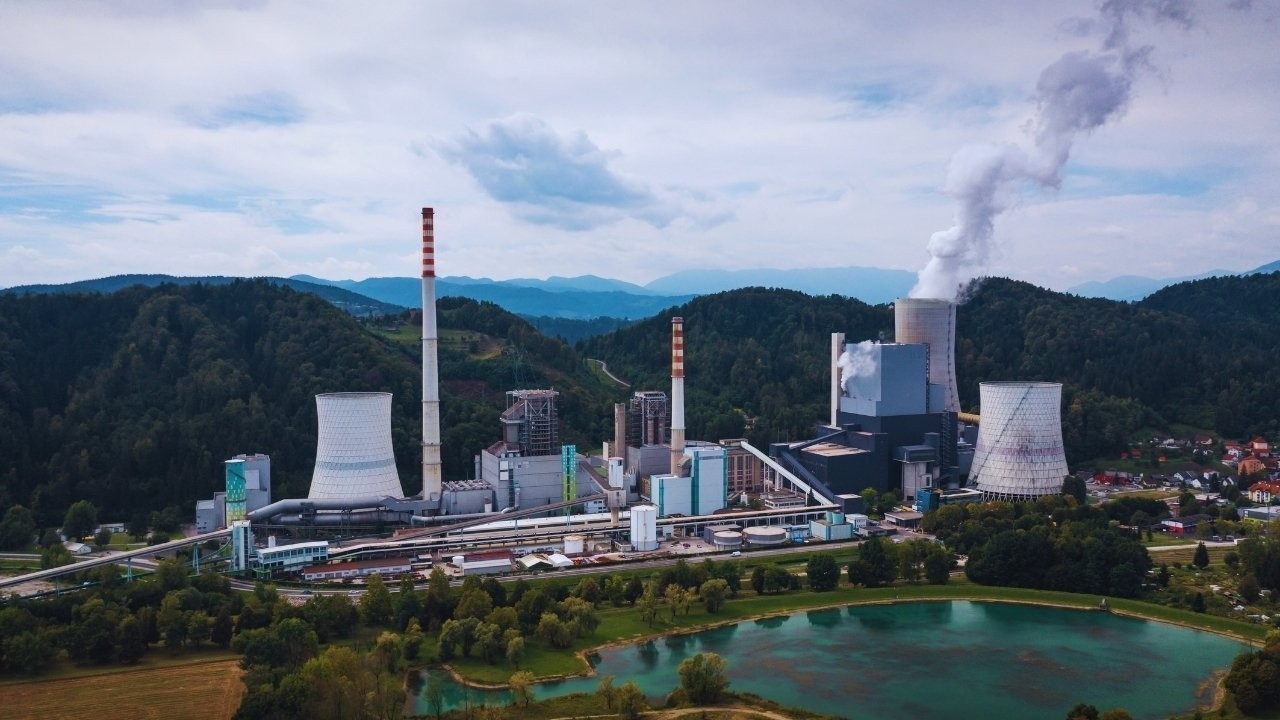

Post by : Anis Karim
As the world accelerates toward solar and wind power, one of the biggest challenges remains energy stability. Sunlight fades, wind fluctuates, and grids struggle to match real-time supply with demand. Traditional batteries help, but they are expensive, short-duration, resource-intensive, and often insufficient for large-scale storage demands.
This is where next-generation thermal storage enters the picture. Unlike chemical batteries, thermal storage holds energy in the form of heat — a proven, long-lasting, and highly scalable method. Today’s advanced systems use molten salts, phase-change materials, crushed stones, liquid metals, and ceramic blocks to store enormous amounts of heat at extremely high temperatures.
The result: low-cost, long-duration, climate-friendly storage solutions that can stabilize grid operations, power entire districts, and support industrial processes around the clock.
Thermal storage is emerging as a critical component of modern renewable grids for several reasons:
it offers long-duration storage at low cost
it reduces reliance on lithium and other mined minerals
it supports both electricity and industrial heat demands
it remains stable and loss-resistant for long periods
it integrates seamlessly with solar, wind, and waste-heat systems
While batteries excel at short-duration stability, thermal storage shines in providing hours, days, and even seasonal backup — a capability essential for clean-energy reliability.
Thermal storage operates on a simple premise: convert renewable energy into heat and store it for later use. This heat can then be re-converted into electricity or used directly for industrial or residential applications.
Key scientific foundations include:
sensible heat storage, where materials like rocks or molten salts store heat by rising in temperature
latent heat storage, which leverages the energy absorbed during phase changes (solid-to-liquid or liquid-to-gas)
thermochemical storage, a newer method using chemical reactions to lock in energy with virtually no loss
These approaches enable storage durations far exceeding traditional battery systems.
Molten salt technology is currently the most advanced and widely adopted form of thermal storage. It is commonly paired with concentrated solar power (CSP) plants that use mirrors to heat salts to high temperatures.
Why molten salts dominate:
they retain heat for long periods
they operate at temperatures above 500°C
they enable night-time solar generation
they convert stored heat into electricity using steam turbines
they have decades of proven performance in utility-scale settings
Next-generation salt mixtures now allow even higher temperatures, enabling efficiency improvements in thermal-to-electric conversion.
Phase-change materials are revolutionizing thermal storage due to their high energy density and compact footprint. PCMs store energy during melting and release it as they solidify.
Popular PCMs include:
paraffin waxes
salt hydrates
metal alloys
bio-based compounds
PCMs are increasingly used in district heating, industrial processes, and building-integrated storage systems due to their stability, scalability, and long life.
An emerging class of storage systems uses crushed stones, refractory ceramics, or composite blocks. These systems heat the materials directly using electricity from solar or wind.
Benefits include:
extremely low cost
abundant, non-toxic materials
high durability and minimal maintenance
storage temperatures exceeding 800°C
Because these systems are simple, rugged, and highly scalable, they are ideal for industrial heat applications and grid-scale storage in diverse climates.
One of the most futuristic developments in thermal storage is the use of liquid metals and high-temperature alloys. These materials can store heat at temperatures exceeding 1,000°C, enabling breakthrough efficiencies.
These ultra-high-temperature systems can:
replace fossil fuels in heavy industries
support metal refining and chemical production
drive high-efficiency turbines for electricity generation
Such systems expand thermal storage beyond power grids into sectors that have historically been difficult to decarbonize.
Thermochemical storage relies on reversible chemical reactions. Energy is stored when a compound is split and released when the compound recombines.
Advantages:
minimal thermal losses
extremely long-duration storage
potential for seasonal energy shifting
compact form factors
This technology is still emerging, but it holds enormous potential for renewable-heavy nations with seasonal energy imbalances.
Grid operators are increasingly turning to thermal storage for its long-duration balancing capability. When wind and solar fluctuate, thermal systems can supply heat or electricity that stabilizes the grid.
Benefits for grid operations:
smoother load management
less curtailment of excess solar and wind
reduced reliance on natural gas peaker plants
consistent output during nighttime
better integration with industrial districts
As grids grow more renewable, thermal storage becomes an essential buffer against variability.
Heavy industries — steel, cement, chemicals, glass — require extremely high temperatures traditionally produced by fossil fuels. Next-generation thermal storage delivers these temperatures cleanly by storing renewable power as heat.
Industries benefit from:
stable, round-the-clock heat supply
reduced emissions
lower operating costs over time
integration with electrified processes
heat-on-demand capabilities
This positions thermal storage as a breakthrough solution for industrial decarbonization.
Thermal storage is also revolutionizing district heating systems in colder regions. Large tanks, underground pits, or salt-based systems store heat generated by solar thermal plants or excess renewable electricity.
These systems support:
residential heating
commercial buildings
hospitals and public infrastructure
heat-sharing microgrids
Community-scale thermal storage improves energy independence and reduces heating costs.
Thermal storage is particularly effective when paired with solar energy. Concentrated solar plants generate powerful heat, but even photovoltaic systems can contribute by directing excess electricity into thermal systems.
Advantages include:
night-time solar energy
reduced need for backup fuels
increased solar plant efficiency
greater grid flexibility
This combination is transforming solar power into a reliable 24/7 energy resource.
Thermal systems have several cost advantages:
inexpensive base materials (rocks, salts, metals)
long system lifetimes
minimal degradation
low maintenance needs
strong scalability without high resource demand
This makes them ideal for nations with limited access to battery minerals or large-scale storage needs for industrial sectors.
Hydrogen production requires heat and electricity. Thermal storage can provide both, enabling efficient hydrogen production during low-cost renewable periods.
Benefits of pairing thermal storage with hydrogen:
improved electrolyzer efficiency
reduced grid strain
balanced renewable use
round-the-clock hydrogen output
This synergy strengthens both sectors as nations move toward zero-carbon fuels.
Thermal storage systems avoid many of the environmental impacts associated with battery mining.
Sustainability benefits include:
minimal rare-metal usage
recyclable core materials
low manufacturing footprint
safe, non-flammable operation
long operational life
These attributes make thermal storage a cornerstone of future green-energy planning.
Despite its advantages, thermal storage still faces obstacles:
high initial development costs for large plants
limited global standards
the need for skilled engineering teams
slower scalability compared to batteries
insufficient policy incentives in some regions
However, rapid innovation and expanding climate commitments are helping overcome these barriers.
Next-generation systems will likely include:
ultra-high-temperature ceramics
advanced metal alloys
next-gen molten salts
modular thermal cubes for buildings
thermal-grid integration tools
AI heat management systems
seasonal heat vaults
Future developments will shape a world where thermal storage becomes as common as solar panels.
Next-generation thermal storage systems are emerging as one of the most important technologies in the clean-energy transition. From grid stability to industrial decarbonization, district heating, and 24/7 renewable supply, these systems provide a scalable, sustainable, and long-duration solution that chemical batteries alone cannot offer.
As nations accelerate climate action and expand renewable infrastructure, thermal storage is poised to become a foundational piece of global energy reliability — delivering steady heat, consistent electricity, and a more resilient future for all.
This article discusses global renewable-energy developments and may not reflect the specific technologies or availability in every region. Energy performance varies based on environment, system design, and policy frameworks.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
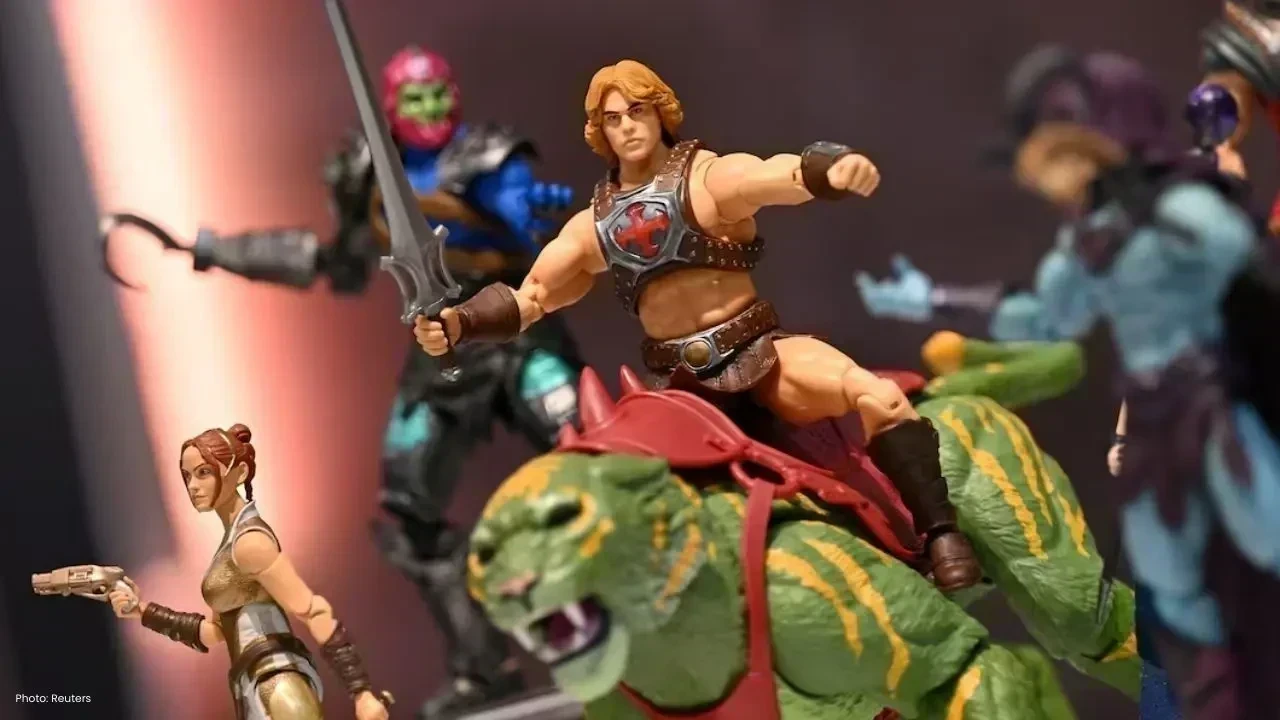

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin