
Post by : Anis Karim
Public libraries across the Middle East are undergoing a quiet revolution. Once seen primarily as repositories of books and quiet study, many libraries are transforming into dynamic technology hubs that serve as incubators for youth learning, creativity, and entrepreneurship. This shift reflects broader social, economic, and technological changes across the region: rising youth populations, growing digital economies, and a renewed policy focus on skills development. The result is a new generation of public institutions that blend traditional literacy with digital fluency, creating accessible pathways for young people to engage with technology, build projects, and connect with mentors and employers.
Libraries are evolving from quiet book stacks into active community centers that host coding bootcamps, robotics clubs, and digital design sessions. For many young people, libraries are now one of the few accessible places to gain hands-on experience with technology. By providing free or low-cost access to hardware, software, and mentorship, these public institutions are lowering barriers to entry for careers in IT and creative industries. The shift also broadens the library’s audience: beyond students and researchers, the modern library welcomes hobbyists, entrepreneurs, and young people seeking career pivot opportunities.
Across the region, libraries have begun offering structured programs targeted at youth development. These often include introductory coding courses, digital media workshops, and entrepreneurship sessions that teach business model basics and pitch skills. Such programs are usually run in partnership with local universities, NGOs, or tech firms, ensuring that content stays current and practical. Participants frequently benefit from project-based learning, where they build a prototype, website, or app by the end of a course, leaving with tangible outcomes to show employers or incubators.
A defining feature of this transformation is the introduction of maker spaces. Equipped with 3D printers, microcontrollers, soldering stations, and design software, maker labs allow youth to prototype physical and digital inventions. These facilities demystify technology: a young person can learn how a circuit works, design a product, and produce a tangible prototype in a single space. This hands-on learning nurtures curiosity, problem-solving, and a do-it-yourself ethic that traditional classroom settings sometimes struggle to cultivate.
One of the most important impacts of tech hubs in libraries is digital inclusion. In many communities, access to high-speed internet, modern devices, and up-to-date software is uneven. Libraries step in to bridge this gap by offering public internet access, device lending programs, and software suites that users might otherwise not afford. For youth from lower-income backgrounds, this access can be life-changing, opening pathways to online courses, remote work opportunities, and global collaboration. By offering structured learning and guidance, libraries help convert access into meaningful skills.
Beyond equipment and courses, libraries are fostering mentorship networks. Volunteer professionals, university students, and local entrepreneurs often serve as mentors, guiding youth through projects and career choices. These relationships are crucial: they provide practical advice, industry connections, and sometimes pathways to internships or jobs. Libraries also host networking events, hackathons, and demo days that connect young creators with potential partners and funders, creating a mini-ecosystem where ideas can be tested, refined, and scaled.
A key to the success of these initiatives is cultural sensitivity. Programs that resonate combine technical skills with cultural relevance—using local languages, addressing community needs, and framing projects in ways that reflect regional priorities. For example, youth may develop apps that map local resources, create educational games based on regional history, or design low-cost solutions tailored to local infrastructure challenges. This grounding ensures that technology serves the community rather than being an imported curiosity.
Public libraries often lack the financial resources to fully equip tech hubs alone. Public-private partnerships have become essential, with tech firms donating hardware, universities contributing curricula, and philanthropic organizations providing grants. These collaborations accelerate the development of facilities and help sustain programs through staff training and resource sharing. Such partnerships can also introduce industry-standard practices into programming, preparing youth for real-world work expectations and bridging the gap between classroom exercises and employer needs.
Several libraries in the region have notable success stories. Graduates of library-based programs have gone on to launch startups, secure scholarships, and attain jobs in software development and digital design. In some cities, library-led initiatives have improved digital literacy rates and increased youth participation in civic tech projects. These outcomes demonstrate that well-designed library programs can generate measurable social and economic benefits beyond the walls of the institution, contributing to employability and local innovation.
Despite early successes, challenges remain. Funding is perennial; initial grants may cover set-up costs, but sustaining programs requires ongoing investment in staff, equipment maintenance, and curriculum updates. Scaling these initiatives to reach rural and underserved areas is another hurdle—urban libraries often pilot programs that rural branches cannot replicate without targeted support. Additionally, libraries must balance their traditional roles with new responsibilities, ensuring that quiet study spaces and archival services continue while tech hubs expand.
Transforming a library into a tech hub requires staff who can manage equipment, teach digital skills, and coordinate partnerships. Many libraries have invested in training existing staff or hiring specialists such as digital facilitators and maker-space coordinators. Continuous professional development is crucial: technology evolves quickly, and staff need ongoing training to keep programs relevant. Equally important is cultivating pedagogical skills—knowing how to support learners with diverse backgrounds and different learning paces.
Governments can accelerate library transformation through policy and funding. National and municipal programs that prioritize digital inclusion, STEM education, and youth employment create an enabling environment for library tech hubs. Some countries have launched service standards and grant schemes specifically aimed at modernizing library infrastructure. When policy aligns with local implementation, libraries become effective delivery points for public skills and inclusion agendas.
Robust monitoring and evaluation help libraries demonstrate impact and attract further funding. Metrics may include the number of program graduates, job placements, startup launches, and community projects completed. Qualitative outcomes—such as increased confidence, social cohesion, and civic engagement—are equally important and often captured through participant stories and community feedback. Collecting and publishing evidence of impact builds credibility and encourages replication in other branches and regions.
Extending services to rural and marginalised youth requires creative approaches. Mobile maker labs, pop-up workshops, and traveling trainers can bring programs to communities without permanent facilities. Partnerships with local schools and community centres amplify reach, while simple, low-cost technology kits enable hands-on learning without heavy infrastructure. Tailoring programs to local contexts—such as agriculture technology for farming communities—ensures relevance and uptake.
As libraries adopt tech equipment, sustainability must be considered. Energy consumption, electronic waste, and resource sourcing are practical concerns. Some libraries implement green practices—using energy-efficient devices, refurbishing donated equipment, and teaching e-waste recycling as part of community programs. These steps align tech education with broader sustainability goals, helping youth learn responsible technology stewardship and the environmental implications of digital growth.
Inclusive programs actively seek to engage girls and young women, who are often underrepresented in tech fields. Libraries can design scholarships, mentorship programs, and women-only workshops to create supportive environments. Showing role models and celebrating diverse success stories help change perceptions and encourage participation. Inclusive programming also accommodates different abilities, ensuring that youth with disabilities can access facilities and learning resources.
Libraries increasingly function as nodes in regional innovation ecosystems, linking universities, incubators, civic groups, and local government. By providing affordable space and community trust, libraries can host pilot projects and early-stage ventures that might otherwise struggle to find support. This ecosystem role amplifies the library’s contribution to local economic development and positions it as a community anchor for innovation.
The future of library tech hubs in the Middle East looks promising. As digital economies mature and youth seek practical, affordable learning pathways, libraries are well-placed to offer inclusive access. Innovations may include virtual reality labs for immersive education, regional digital archives co-created by youth, and micro-credential programs accredited by local institutions. Critical to success will be sustained funding, pragmatic partnerships, and ongoing community engagement that ensures programs remain locally relevant.
Public libraries in the Middle East are reinventing themselves as accessible technology hubs that empower youth with skills, mentorship, and community connections. While challenges around funding, scale, and sustainability remain, the transformative potential of these spaces is clear. By centring local relevance, fostering partnerships, and measuring impact, libraries can continue to play a pivotal role in preparing young people for the digital age and contributing to broader social and economic development. To maximise their reach, many libraries are experimenting with blended learning models that combine self-paced online modules with in-person coaching. These hybrid approaches allow youth to progress at their own speed while still benefiting from hands-on support during scheduled maker sessions. Libraries also curate open educational resources and offer guided pathways that map beginner modules to more advanced training, creating clear progression routes from basic digital literacy to specialised skills.
Funding innovation continues to evolve as well. Beyond one-off donations, some libraries have adopted social enterprise models, charging modest fees for advanced workshops while keeping core services free. Revenue from paid courses can subsidise outreach and equipment upgrades, creating a degree of financial resilience. Micro-sponsorships—small recurring contributions from local businesses or alumni—also provide steady support and foster deeper community ties. Libraries that demonstrate strong outcomes attract a broader range of partners, from municipal bodies to private sector sponsors, enabling long-term planning and expanded programming.
Finally, the human dimension remains central. Youth benefit not only from technology but from the safe, trusted environment libraries offer. For many, libraries are neutral spaces where diverse communities can gather, learn, and innovate together. This social fabric matters: it supports the resilience of young people facing uncertain job markets, provides a sense of belonging, and amplifies the impact of technical skills through collaboration and civic engagement. As libraries continue to adapt, their success will hinge on combining practical training with community stewardship, responsive governance, and genuine youth participation. Strategic planning and community feedback loops will determine which services scale fastest. When young people shape programming through advisory panels, participation increases and outcomes improve. Libraries that embed youth voice in governance not only design better programs but also nurture future civic leaders who will champion inclusive tech access for the next generation. Sustained commitment from all stakeholders will be essential for long-term success and community trust.
This article provides a general overview based on recent trends and illustrative examples. Specific outcomes vary by institution and locality. Readers should consult local library announcements or authorities for detailed, up-to-date information.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
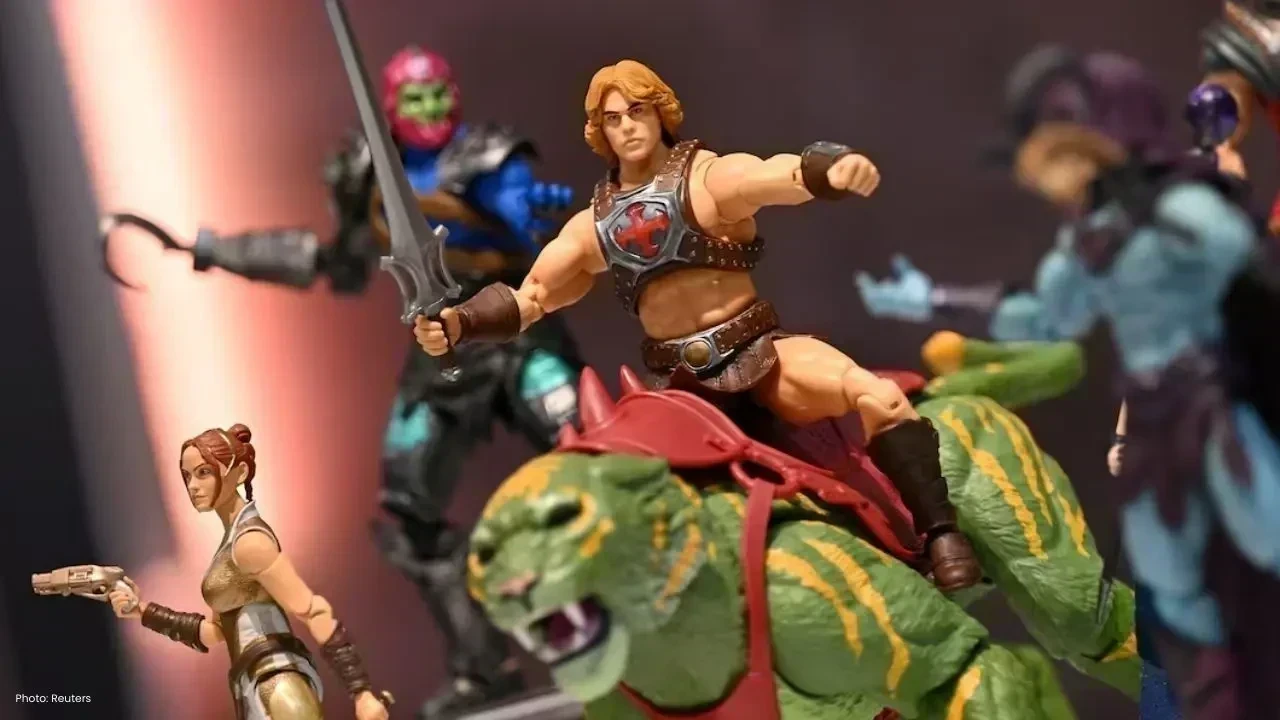

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin