
Post by : Naveen Mittal
Universities and higher education institutions are increasingly pursuing international campus expansion as part of their globalization strategies. Establishing branch campuses abroad, or cross-border educational expansion, allows institutions to reach new student markets, enhance global reputation, and foster academic collaborations. In regions such as Dubai and India, recent developments show how cross-border colleges and universities are evolving rapidly. This article investigates the motives, global trends, case studies, challenges, strategies, and best practices for successful university campus expansions across borders.
By opening branch campuses in foreign countries, universities tap into local student demand who may prefer international credentials but cannot relocate abroad. This expands enrollment and revenue streams.
International presence helps universities enhance global visibility, improve rankings, and attract international faculty, research partnerships, and funding.
Relying solely on home country enrollment is risky—diversifying across countries helps buffer against demographic changes, regulatory shifts, or local economic downturns.
Branch campuses foster partnerships with local institutions, industry, and research centers, enabling joint programs, faculty exchange, and localized research projects.
Universities can adapt their programs to local contexts, languages, and industry needs, which helps blend global standards with regional relevance.
Dubai is emerging as a higher education hub. Many Indian and international institutions see Dubai as a strategic location to establish overseas campuses. Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad (IIM Ahmedabad) recently launched its first international campus in Dubai, marking a key milestone in India-UAE knowledge collaboration. The campus is located in Dubai International Academic City and offers MBA programs designed for regional professionals.
In UAE, regulatory support, infrastructure, incentives, and strategic vision (e.g., “Education 33”) encourage foreign institutions to establish campuses. Dubai’s goal to increase international student enrollment makes it attractive for branch campus development.
Also, BITS Pilani has a Dubai campus—one of the earlier Indian universities to set up an overseas campus. The BITS Dubai campus offers undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral programs in engineering and business and serves students from the Gulf region as well as India.
Recently, foreign universities are seeking to open branch campuses in India. The Indian government relaxed regulations allowing foreign universities to operate legally inside India. For example, a number of UK universities have plans to open campuses in India to tap into large student markets and reduce the barrier of overseas mobility.
This trend indicates a reverse flow: instead of students always going abroad, universities come into India, bridging global education and local access.
Some institutions are adopting hybrid expansion: combining online programs, satellite teaching centres, local study centres, or micro-campuses in multiple regions. For instance, online education firms are partnering with universities to deliver blended degree programs in multiple geographies.
EdTech platforms also serve as enablers, connecting students in one country with faculty and resources in another, effectively creating “virtual campuses” across borders.
A fully autonomous or semi-autonomous campus offering complete degree programs, with faculty, facilities, and accreditation in the host country. This is the classical branch campus model.
The parent university partners with a local institution (university, government, private college) to deliver degree programs. The local entity handles regulatory compliance, while the foreign partner provides curriculum, branding, and academic oversight.
Smaller footprint campuses (for specific faculties, research, or executive education) rather than full-fledged universities. These may offer selected programs or serve as regional study centres.
The university grants license or franchising rights to a local institution to offer degree programs under its brand, with curriculum alignment, quality monitoring, and certification.
Instead of physical campuses, institutions set up teaching hubs, online programs, or mixed modalities that allow students to access courses globally while doing some in-person modules locally.
Institutions can recruit students from both the host country and neighboring regions.
New tuition streams, research funding, grants, and local government incentives support financial viability.
Students and faculty can benefit from cross-cultural learning, mobility, and joint research opportunities.
Adapting global curricula to local market needs can make education more applicable and attractive to students in host countries.
Branch campuses help build local talent, facilitate industry collaboration, and increase a university’s influence in regional education policy.
Each country has its own laws concerning foreign universities, recognition of degrees, quality assurance, and local education policies. Navigating this complexity is one of the major barriers.
Setting up infrastructure, hiring qualified faculty, maintaining quality standards, and running operations abroad requires significant capital and ongoing investment.
Universities must adapt curriculum, pedagogy, support services, and campus culture to local expectations while maintaining brand identity.
Attracting and retaining qualified faculty in the new location is tough, especially when competing with local and international offers.
Ensuring that branch campuses deliver academic standards equivalent to the home campus is critical. Disparities damage reputation.
If the branch campus fails to perform academically or financially, it can harm the reputation of the parent institution globally.
Demand for certain programs may be lower than expected, or competition from local universities may be intense.
Perform market research to understand demand, demographics, competition, and regulatory environment.
Assess cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic factors.
Conduct financial modeling and risk analysis.
Study host country’s laws on foreign institutions, accreditation, degree equivalence, approvals, and local partnerships.
Secure early meetings with education ministries, accreditation agencies, and regulatory bodies.
Plan for dual accreditation or recognition across countries.
Identify credible local partners—universities, government, private institutions.
Negotiate agreements covering governance, cost sharing, curriculum responsibilities, and branding.
Define roles: who handles facilities, hiring, student services, academic oversight.
Map which degree programs to offer based on market needs.
Adapt pedagogical methods, course contents, assessments, and support services to local context.
Ensure quality control, alignment with home institution standards, and local relevance.
Build or lease suitable campus infrastructure (classrooms, labs, housing, support services).
Recruit faculty: a blend of home-campus staff, local hires, visiting professors, and adjuncts.
Develop faculty support, training, and integration to institutional culture.
Brand the new campus—local marketing, open houses, digital outreach.
Offer scholarships, exchange programs, articulations, dual degrees.
Start with a pilot cohort or smaller programs before full scale.
Track performance metrics: student retention, graduation rates, faculty satisfaction, finances, regional impact.
Make iterative improvements.
Expand offerings progressively, scale operations, introduce research units, or additional branches.
IIM Ahmedabad recently launched its first overseas campus in Dubai, situated in Dubai International Academic City. The campus began with a one-year MBA program targeted at professionals in the region, reflecting the strategic importance of the Gulf as a student market. This expansion signifies a deepening of India-UAE educational ties and advances the global reach of Indian higher education.
IIFT announced its first overseas campus in Dubai, aligning with India’s national policy of educational internationalization. The campus is approved through necessary regulatory clearances and will offer trade, business, and economics programs, tapping Gulf demand and fostering cross-border education.
BITS Pilani’s Dubai campus, established decades ago, is one of the prominent examples of Indian universities expanding overseas. The campus offers engineering and business degrees, enrolls students from across the Gulf, and operates under local educational authority approvals. This model demonstrates long-term sustainability of branch campuses when aligned with regional demand.
Start with small pilot programs before expanding to full campuses.
Choose locations with demand, regulatory friendliness, infrastructure readiness, and strategic importance.
Prioritize partnerships with local credible institutions or governments to ease regulatory and operational burdens.
Maintain rigorous quality assurance and consistent academic standards across campuses.
Provide cultural, administrative, and academic orientation support for students and faculty.
Use adaptive curriculum localization while retaining core identity and excellence.
Monitor performance metrics, student feedback, and market shifts continuously.
This article is for general informational purposes only. Institutional expansion plans, policies, and regulatory conditions vary by country and over time. Before pursuing any international campus development, consult relevant education authorities, legal counsel, and conduct localized feasibility studies tailored to your institution’s needs.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
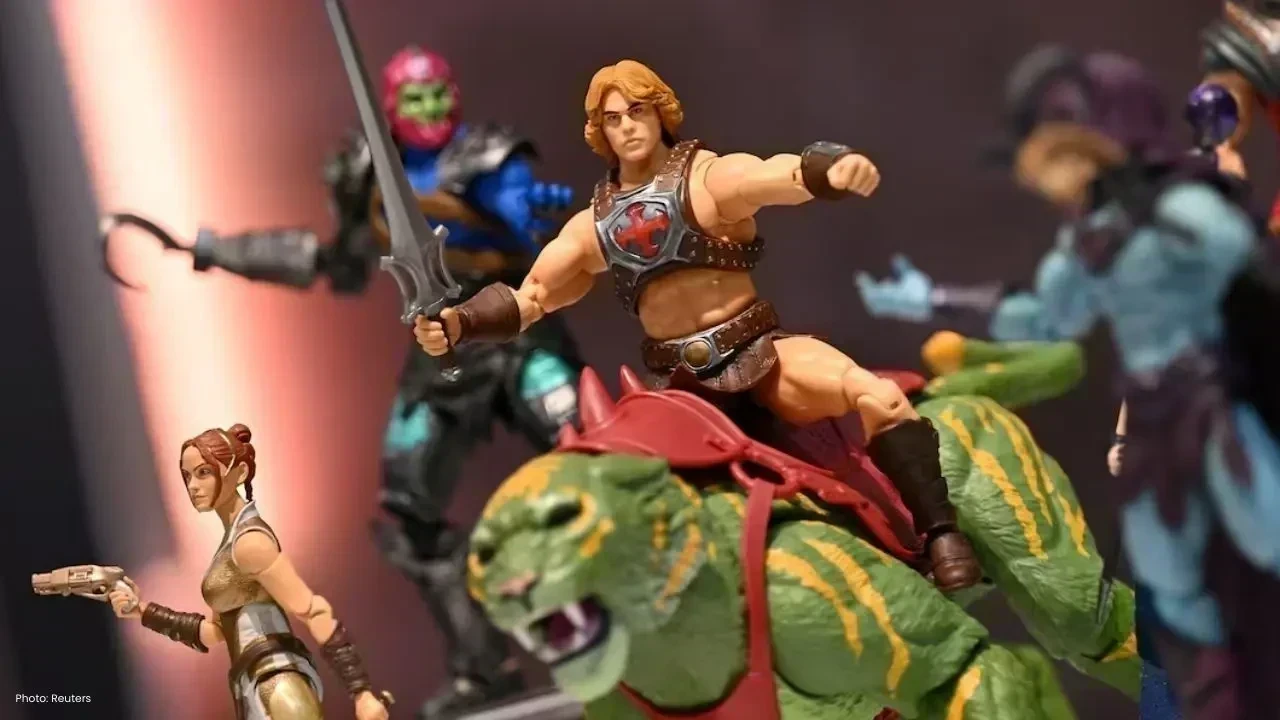

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin