
Post by : Anis Karim
Cancer research is evolving at a pace few could have anticipated a decade ago. Among the advancements making headlines this week is a breakthrough offering fresh hope to patients whose tumours have become resistant to traditional treatments. Scientists have reported early success in disabling a gene called NRF2—an influential driver of chemotherapy resistance in several cancers. By switching off this gene in specific tumour cells, researchers observed renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs, opening a potential pathway to more effective, personalised cancer care.
For patients, families, and clinicians dealing with the unpredictable reality of cancer, this development raises essential questions: What does this mean for treatment landscapes? How soon might this become accessible? And what should patients ask their doctors today to stay prepared? This article delves into the science, the possibilities, and the practical implications.
Chemotherapy resistance remains one of the most challenging hurdles in cancer treatment. Tumours initially respond to drugs, but over time, many develop mechanisms to protect themselves from these therapeutic agents. NRF2 is one of the central regulators in this process. When improperly activated or mutated, it enables tumour cells to neutralise chemotherapy’s effects and continue multiplying.
The recent research specifically targeted a mutation of this gene using modern gene-editing tools. Disabling the NRF2 mechanism in tumour cells restored their vulnerability to common chemotherapy drugs. In addition to drug sensitivity, researchers observed slower tumour growth—an encouraging sign that targeting this pathway could dramatically shift outcomes.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the study is the precision with which scientists edited tumour cells. Instead of blasting all cells indiscriminately, researchers used highly targeted gene-editing tools that modified only tumour cells with the specific mutation. Even more impressive: editing only a portion of the cancer cells, rather than all of them, still improved responsiveness to chemotherapy.
This level of precision reduces the likelihood of unwanted genetic changes and supports the broader trend of personalised oncology—where treatments are tailored to the biology of each patient’s disease rather than relying on generalised protocols.
While the study was conducted on lung squamous cell carcinoma, NRF2 involvement extends to a wide range of cancers. Tumours of the liver, oesophagus, head and neck, and several other organs also display NRF2-driven resistance patterns. This suggests the breakthrough could have implications far beyond a single cancer type.
Patients facing chemotherapy resistance often encounter a decline in options. Once a tumour stops responding, further treatment becomes more complicated, more toxic, and often less effective. If tumour sensitivity can be restored, many patients may regain access to treatment pathways that were previously ruled out.
When standard treatments fail, oncologists frequently turn to stronger drug combinations or aggressive salvage therapies. These can bring heavy side-effects and compromise quality of life. If existing therapies regain their potency through NRF2-targeted approaches, patients may avoid these harsher alternatives.
Cancer is no longer treated as a single disease—it is understood as a complex group of disorders requiring individualised strategies. This breakthrough reinforces the importance of molecular testing. As precision therapies advance, identifying how each tumour behaves at the genetic level becomes essential.
If future therapies can influence resistance pathways, treatment planning may become more adaptive. Instead of waiting for resistance to appear, oncologists may eventually anticipate it and intervene pre-emptively.
This breakthrough, though early, invites important conversations between patients and their medical teams. Here are essential questions every patient or caregiver should consider:
Understanding whether your tumour activates pathways like NRF2 helps in anticipating treatment challenges and identifying future therapeutic opportunities.
Modern oncology increasingly relies on genetic insights. If a tumour hasn’t been tested recently—or if it has changed over time—updated analysis may open new doors.
While this NRF2-focused method is not yet in human trials, similar precision medicine studies are ongoing. Asking early ensures you are aware of potential eligibility.
Doctors use various tools—scans, blood markers, liquid biopsies—to monitor how tumours respond. Knowing the plan helps patients stay informed and engaged.
Preparing for future scenarios brings clarity and reduces distress later. Understanding the next lines of therapy helps patients make informed decisions.
While promising, such therapies involve risks and unknowns. Asking about benefits, timelines, and realistic expectations is essential.
Even when medical breakthroughs occur, accessibility can vary. Early discussions help patients prepare financially and logistically.
Although the research is exciting, it is still in pre-clinical stages. Human trials must confirm that the therapy is safe, effective, and durable. This process can take several years, depending on results.
Cancer treatment is shaped by numerous factors—genetic mutations, tumour location, stage, patient health, and more. Even with NRF2 targeting, outcomes will differ from patient to patient.
Cancer rarely responds to a single therapy. Even with advanced gene-editing solutions, oncologists will likely combine chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted drugs, and supportive therapies.
Gene-editing technologies are powerful tools, but their long-term implications must be thoroughly studied. Off-target effects, immune reactions, and delivery challenges all require careful oversight.
Advanced cancer treatments are often expensive and difficult to distribute widely. Ensuring fair access across low- and middle-income countries will be critical to the success of any new therapy.
Researchers plan to begin early-phase clinical trials once safety, dosage, and delivery questions are fully addressed in the laboratory. These initial trials will focus strongly on safety and feasibility.
Because NRF2 impacts several cancers, scientists expect new studies to explore its relevance in other aggressive tumours.
The research used lipid nanoparticles—a delivery approach widely appreciated for its precision and safety profile. Expect future studies to refine how gene-editing tools are delivered into the body.
Instead of replacing existing therapies, NRF2-targeting may work best when combined with treatments that optimise the immune system and disrupt tumour growth patterns.
As gene-focused therapies grow, the demand for advanced diagnostics, tumour sequencing, and real-time monitoring will increase. Patients may see molecular testing become a standard part of their care journey.
The findings represent a shift toward interventions that modify tumour behaviour instead of solely relying on new drug development. By resetting the tumour’s sensitivity to chemotherapy, this breakthrough demonstrates how gene-targeted solutions can revive existing therapies and reduce the burden of treatment.
It also reflects a broader transformation within oncology:
More personalised care
Earlier and more precise diagnostics
Fewer blanket treatment approaches
Greater adaptability when resistance emerges
For patients and caregivers, this evolution means greater hope—not only in the form of future cures but in the possibility of more manageable and effective treatment journeys.
Targeting the NRF2 gene represents a bold step forward in addressing one of cancer’s most stubborn challenges: chemotherapy resistance. While this new approach is still in its early stages, the clarity and promise of the results suggest a major shift in how resistant cancers might be treated in the coming years.
Patients, families, and healthcare providers should stay informed, remain engaged in treatment discussions, and explore emerging research and trial opportunities. As precision medicine advances, breakthroughs like this bring the medical community closer to treatments that are not only more effective but also more personalised, safer, and sustainable.
This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be treated as medical advice. Patients should always seek guidance from qualified healthcare professionals.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
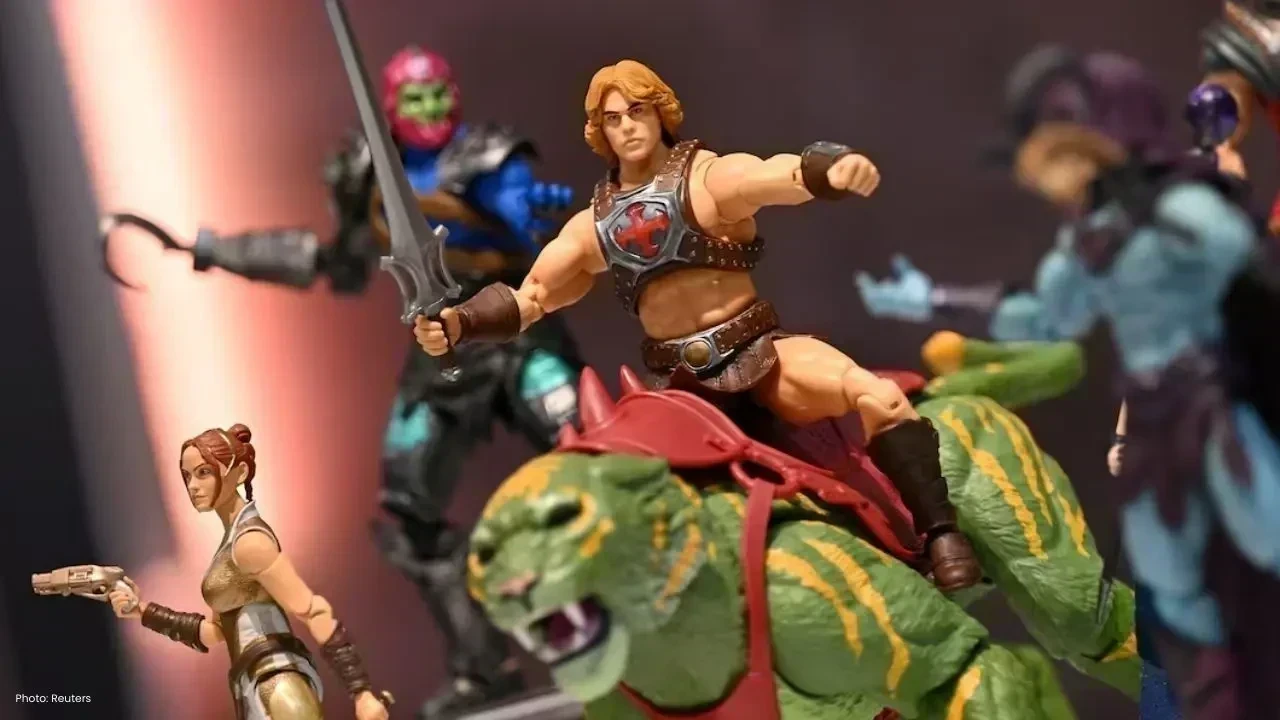

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin