
Post by : Anis Karim
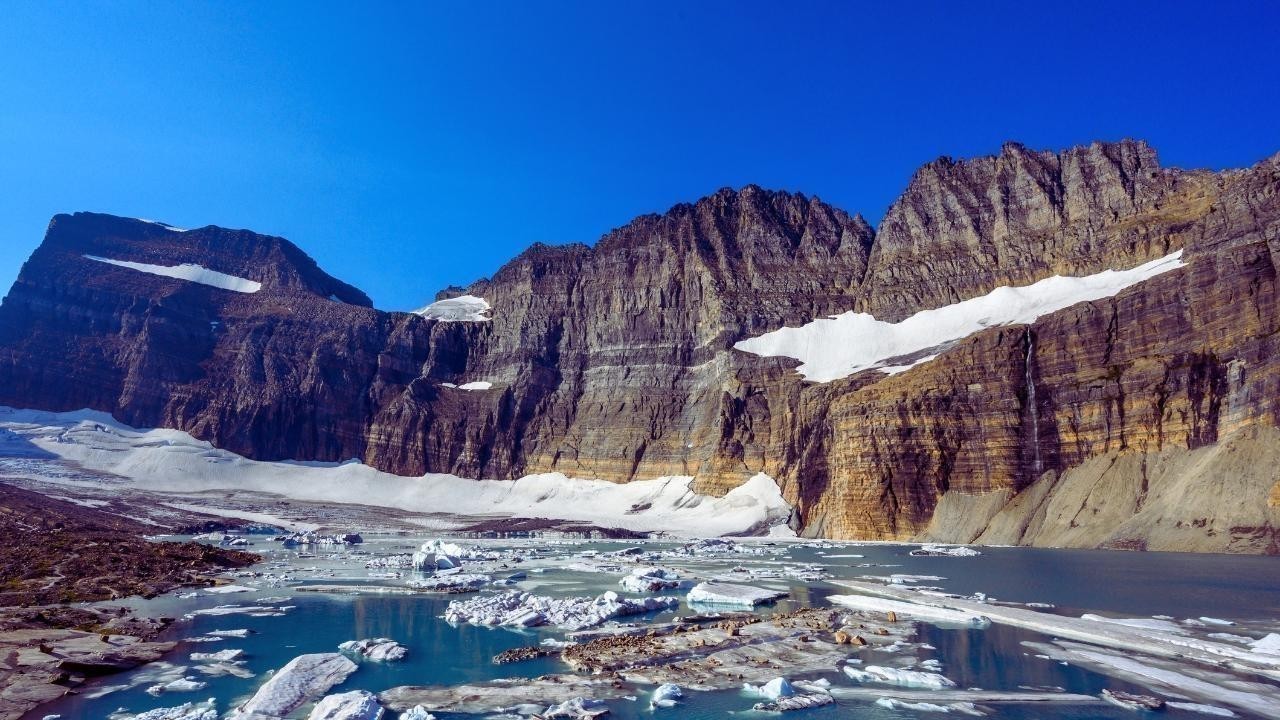
Towering over Asia, the Himalayas are more than just mountains—they're the water towers of nearly two billion people. But what was once a frozen fortress is now melting at an alarming rate. In 2025, scientists are warning that the Himalayas are warming at nearly twice the global average, triggering a cascade of environmental, social, and political consequences.
From disappearing glaciers to flash floods, the changes unfolding in this high-altitude region offer a dramatic glimpse into the future of global climate disruption. The world may focus on sea-level rise or heatwaves, but what’s happening in the Himalayas is just as urgent—and possibly more dangerous.
Glaciers in the Himalayas are disappearing faster than ever. According to recent studies, the region has lost over 40% of its ice mass in the past five decades, with the pace accelerating significantly since 2000. The culprit is a combination of rising temperatures, soot from industrial activity, and shifting weather patterns.
By 2100, up to two-thirds of Himalayan glaciers could be gone if current emission rates continue. This isn’t just a loss of scenic beauty—it’s a direct threat to rivers like the Ganges, Indus, Brahmaputra, Yangtze, and Mekong, which originate in these mountains. These rivers are lifelines for agriculture, drinking water, and industry across South and Southeast Asia.
Glacial meltwater sustains flow during dry seasons. As glaciers shrink, seasonal water scarcity could become the new norm in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and beyond. The result? Increased pressure on irrigation systems, drinking water access, and cross-border river-sharing agreements.
The impacts of warming in the Himalayas are not limited to melting ice. Climate volatility is triggering more frequent and intense weather events across the region. In 2023 alone, Nepal witnessed its worst-ever monsoon-triggered landslides, while Bhutan recorded flash floods that swept away entire settlements.
Permafrost, once stable in the upper reaches, is now thawing rapidly, destabilizing mountain slopes and infrastructure. Entire villages in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh have had to relocate due to erosion and water scarcity.
As weather patterns shift, snowfall becomes unpredictable. Areas that once saw snow for 6–8 months now go snowless for weeks during winter, threatening ecosystems and traditional livelihoods such as yak herding and mountain agriculture. Local biodiversity—from high-altitude flora to endangered snow leopards—is being pushed toward extinction.
The Himalayas serve as a strategic water source across international boundaries, and as resources dwindle, tensions are rising. India and China, for instance, have long-standing disputes over water usage along the Brahmaputra River. Climate stress adds fuel to these disagreements.
In 2024, satellite imagery confirmed that several Himalayan glacial lakes had swollen beyond safe limits, raising fears of glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). These sudden events can devastate downstream areas with little warning. Countries like Nepal and Bhutan have had to install early warning systems, but coverage is still limited.
Transboundary water treaties in South Asia—many established decades ago—are not equipped to handle the rapidly changing realities of Himalayan hydrology. A lack of real-time data sharing and political mistrust hampers coordinated climate response.
The Himalayas are not just physical landmarks—they are sacred spaces. From Mount Kailash to the Gangotri Glacier, these mountains hold deep spiritual meaning for Hindus, Buddhists, and indigenous communities. Melting glaciers and retreating snowlines are erasing centuries-old pilgrimage paths and reshaping religious landscapes.
Local mountain communities who have lived sustainably for generations are now facing existential decisions: migrate, adapt, or perish. Traditional knowledge systems, already marginalized by modern policy, are struggling to keep pace with the speed of ecological collapse.
Festivals tied to seasonal snowmelt or sacred river origins are being disrupted. For many, this cultural loss is just as painful as environmental degradation.
Tourism in the Himalayas brings income but also increased ecological pressure. Trekking trails, mountain roads, and infrastructure projects are booming post-pandemic as domestic travel in India, Nepal, and Bhutan surges.
However, this growth comes at a cost. Overcrowding, plastic pollution, and unregulated construction are straining fragile ecosystems. Popular destinations like Manali, Leh, and Pokhara now face waste disposal crises and water shortages.
Hydroelectric dams, often promoted as green energy alternatives, have displaced communities and altered river flow. While these projects aim to reduce fossil fuel dependency, their ecological footprint in a delicate mountain region remains controversial.
Despite the crisis, there are rays of hope. Himalayan nations are investing in climate science like never before. Bhutan is setting an example with its carbon-negative policies and reforestation programs. Nepal is digitizing glacial monitoring and expanding early-warning systems for flash floods.
Community-led conservation models are gaining traction. In Sikkim, villagers are restoring alpine meadows and building check dams to conserve meltwater. In Ladakh, artificial ice reservoirs called “ice stupas” are being used to provide water in early summer when traditional sources run dry.
International collaboration is also increasing. Initiatives like the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) are helping standardize data collection and coordinate regional adaptation strategies. But many experts argue that without deeper political will and stronger funding, these efforts may fall short.
What happens in the Himalayas doesn’t stay in the Himalayas. The region's accelerated warming is a stark preview of what lies ahead for other parts of the planet. Its glaciers are not just local assets—they’re global indicators.
The crisis challenges our understanding of resilience. These mountains have stood for millennia, weathering ice ages and tectonic shifts. But now, they are vulnerable—not because of nature, but because of human inaction.
The future of Asia’s great rivers, ecosystems, and cultures may well depend on what actions are taken today. Protecting the Himalayas is no longer a local issue—it’s a planetary imperative.
This article is for informational purposes only and reflects climate science and developments as of 2025. Readers are encouraged to consult local environmental agencies and scientific institutions for updates.

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

10 Songs That Carry the Same Grit and Realness as Banda Kaam Ka by Chaar Diwari
From underground hip hop to introspective rap here are ten songs that carry the same gritty realisti

PPG and JAFZA Launch Major Tree-Planting Drive for Sustainability
PPG teams up with JAFZA to plant 500 native trees, enhancing green spaces, biodiversity, and air qua

Dubai Welcomes Russia’s Largest Plastic Surgery Team
Russia’s largest plastic surgery team launches a new hub at Fayy Health, bringing world-class aesthe

The Art of Negotiation
Negotiation is more than deal making. It is a life skill that shapes business success leadership dec
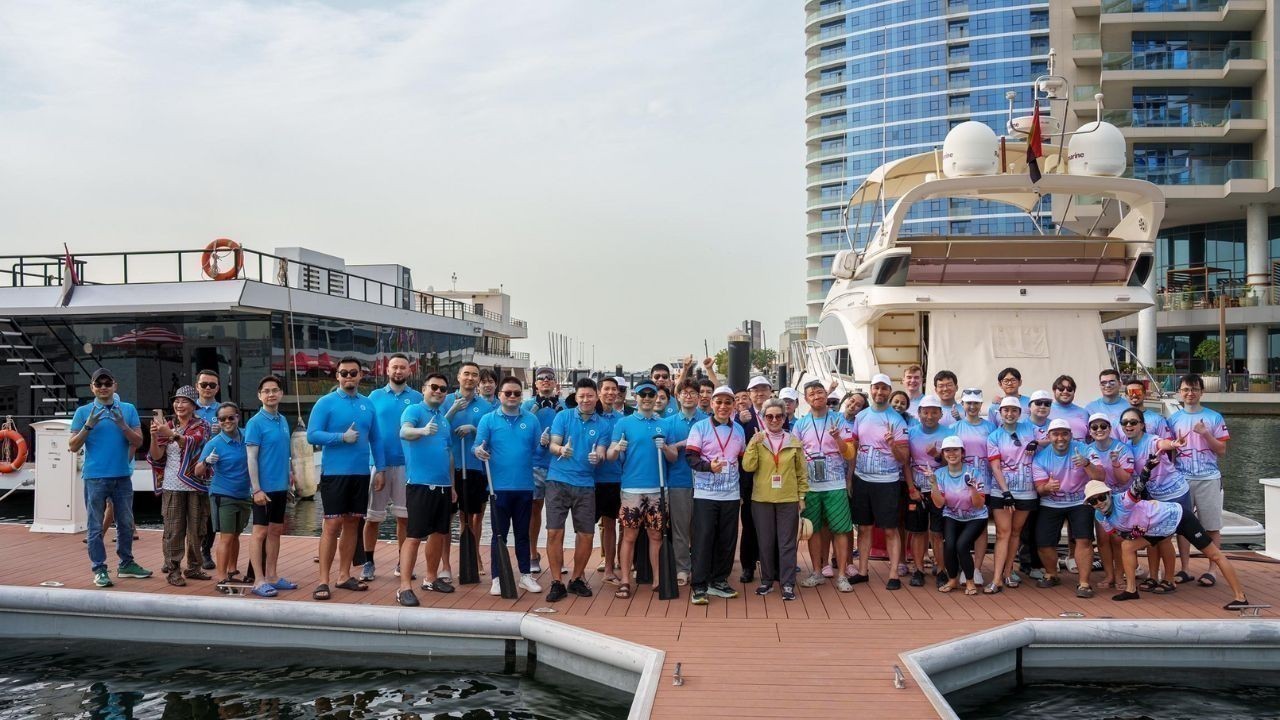

Hong Kong Dragon Boat Challenge 2026 Makes Global Debut in Dubai
Dubai successfully hosted the world’s first Hong Kong dragon boat races of 2026, blending sport, cul

Ghanem Launches Regulated Fractional Property Ownership in KSA
Ghanem introduces regulated fractional real estate ownership in Saudi Arabia under REGA Sandbox, ena

Winter Skin Care: 10 Hydrating Drinks That Give Natural Glass Skin Glow
Learn how simple winter drinks keep your skin hydrated reduce dryness and support a natural glass sk

Why Drinking Soaked Chia Seeds Water With Lemon and Honey Before Breakfast Matters
Drinking soaked chia seeds water with lemon and honey before breakfast may support digestion hydrati
Morning Walk vs Evening Walk: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Morning or evening walk Learn how both help with weight loss and which walking time suits your body

What Really Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Daily
Discover what happens to your body when you drink lemon turmeric water daily including digestion imm

DXB News Network Presents “Ctrl+Alt+Wim”, A Bold New Satirical Series Starring Global Entertainer Wim Hoste
DXB News Network premieres Ctrl+Alt+Wim, a bold new satirical micro‑series starring global entertain

High Heart Rate? 10 Common Causes and 10 Natural Ways to Lower It
Learn why heart rate rises and how to lower it naturally with simple habits healthy food calm routin

10 Simple Natural Remedies That Bring Out Your Skin’s Natural Glow
Discover simple natural remedies for glowing skin Easy daily habits clean care and healthy living ti
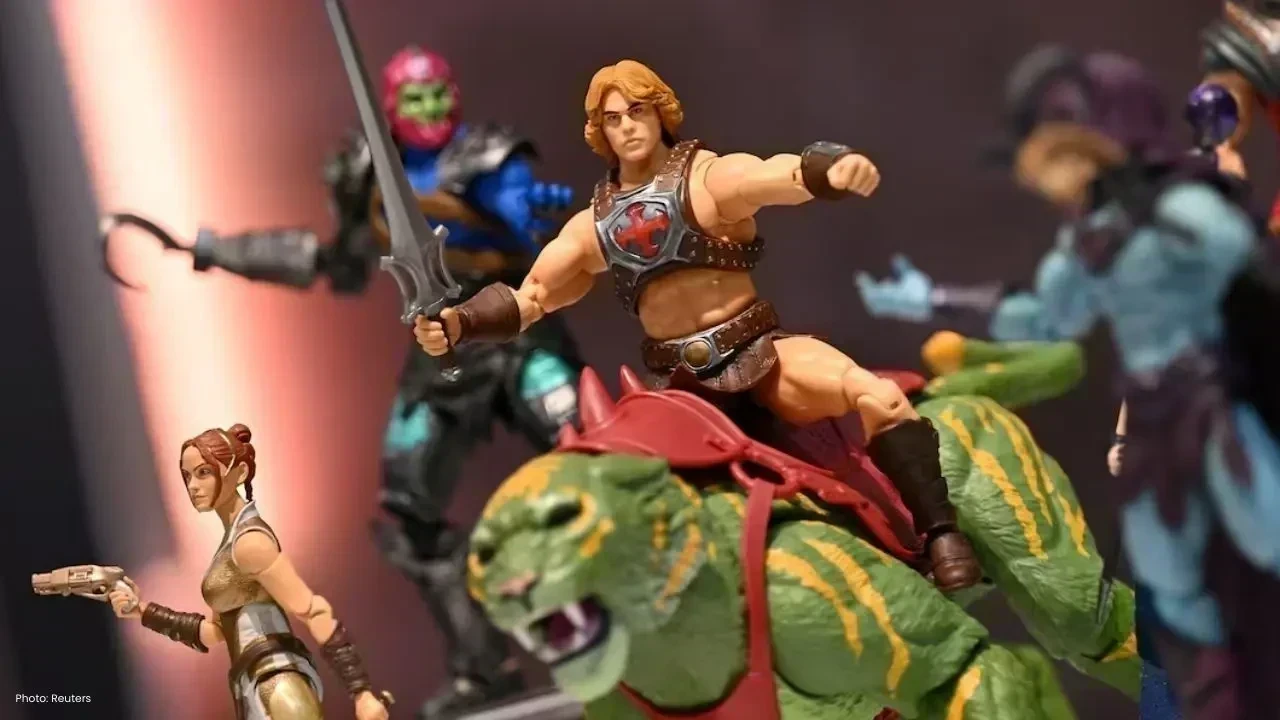

Mattel Revamps Masters of the Universe Action Figures for Upcoming Film
Mattel is set to revive Masters of the Universe action figures in sync with their new movie, ignitin